The 2007 – 2009 Financial Crisis Explained
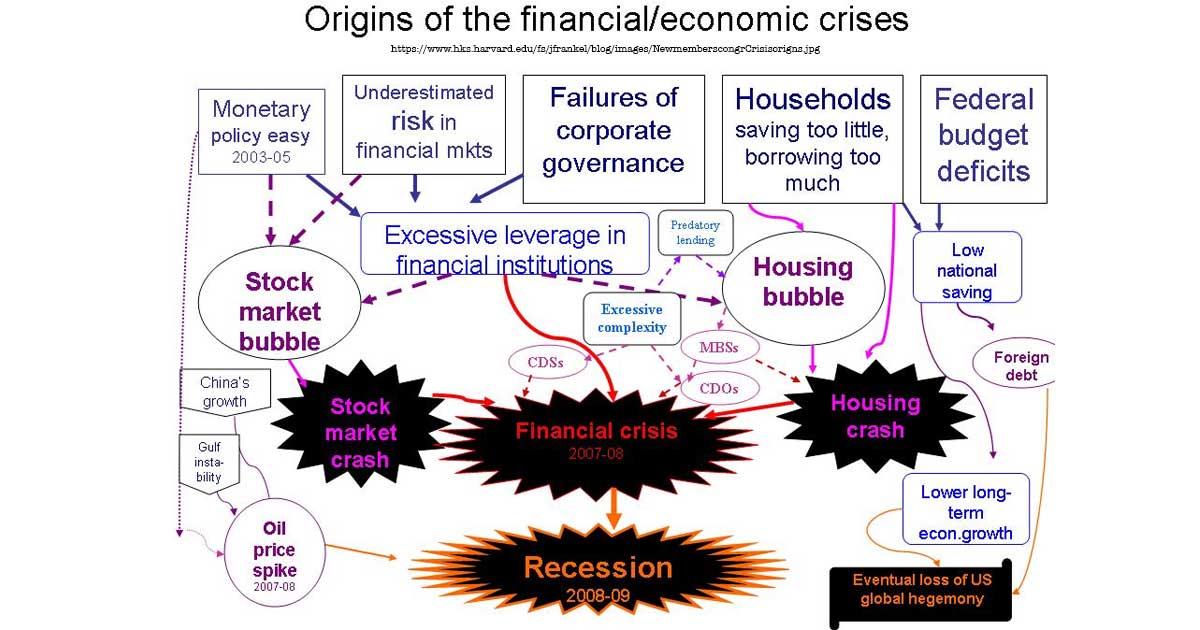
We explain the Financial Crisis / Great Recession of 2007 – 2009 that began with the 2006 housing bubble, led to a recession in the U.S. by December 2007, and became a global crisis by 2009.
Economics is the social science that studies the production, distribution, trade, and consumption of goods and services. Economics uses a mix of psychology, mathematics, experiment, and analysis to predict and understand economies.

We explain the Financial Crisis / Great Recession of 2007 – 2009 that began with the 2006 housing bubble, led to a recession in the U.S. by December 2007, and became a global crisis by 2009.

Below we present an annotated version of Andrew Carnegie’s 1889 essay Wealth (better known as the Gospel of Wealth).

Politics can be treated as a science (political science), but it must always seek data that can be confirmed by our senses (empirical evidence).

In practice, human action often has paradoxical or unintended effects. Sometimes effects or side effects even have the exact opposite effect as intended.

We examine the historical effects of social, political, and economic inequality on society to see how it has led to social unrest and events like revolutions and populist uprisings.

The rise of piracy and the birth of the public stock market roughly intersect, this is because the first public stocks were essentially a type of insurance against pirates.
In 1602, the Dutch East India Company (VOC) became the first publicly traded company when it sold shares on its own Amsterdam Stock Exchange (the first stock market).

There are different types of capital, value, commodities, and markets including natural, human, social, manufactured, and financial.

Game theory involves games, but it isn’t the study of games. It is the study of mathematical models of conflict and cooperation regarding decision making.

For a given market, the choice always boils down to state intervention vs. the free-market, there is no third option (unless you count mixed-markets).