The Economy of Words

The Economy of Words: The art of communication using all symbolic measures afforded by technology. Or, how to communicate effectively and participate in the information economy, with thrift, despite the tyranny of the terms.
Philosophy is the study of the natural and theoretical nature of knowledge, reality, existence, and being. Philosophy can broken down into categories based on subject and technique. See the branches of philosophy.

The Economy of Words: The art of communication using all symbolic measures afforded by technology. Or, how to communicate effectively and participate in the information economy, with thrift, despite the tyranny of the terms.

In his Republic, Plato examines how Democracy can lead to Tyranny in a republic. We explain Plato’s theory as it pertains to democracy and tyranny.

The problem with unsubstantiated information is that it is unverified as true, and often leaked by sources with plausible deniability, which is confusing.

Thomas Jefferson is credited with having said, “equal rights for all, special privileges for none,” a slogan that other progressive Democrats like Williams Jennings Bryan embraced.

Although we can consider Jeremy Bentham the founder of modern Utilitarianism, and his successor John Stuart Mill the one who popularized it, early Greek philosophers like Aristotle, Aristippus and Epicurus presented the original Utilitarian / Consequentialist / Greatest Happiness theories.

On this page we discuss the concepts of fairness, justice, morality, and ethics as they relate to Utilitarianism.

We explain how experience and social interactions shape our frame of reference and create ideological bubbles, and how this creates confirmation bias and “bubble filters” that reinforce these bubbles.
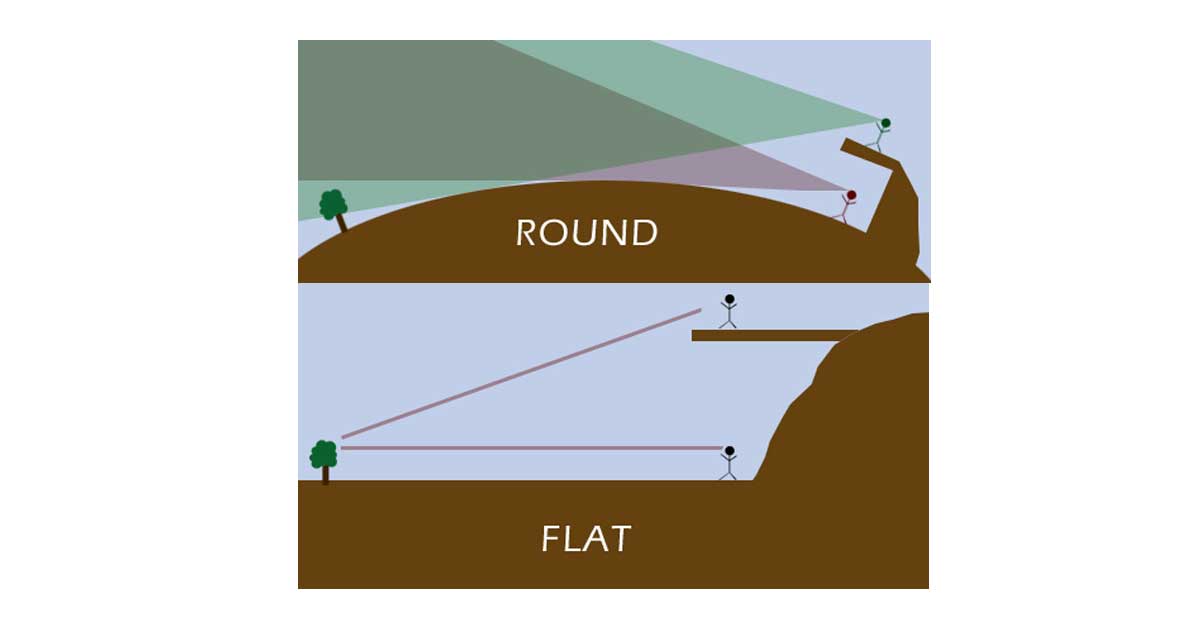
Reason is the application of “pure logic”, empirical evidence, experiment, and skepticism to find truths, facts, and theories (AKA “critical thinking”).

Social Capitalism can be defined as a socially minded form of capitalism, where the goal is doing social good, rather than just the accumulation of capital.
Liberalism is the political ideology of liberty and equality, where classical liberalism emphasizes individual liberty and social liberalism emphasizes social equality.