Hume’s Fork Explained
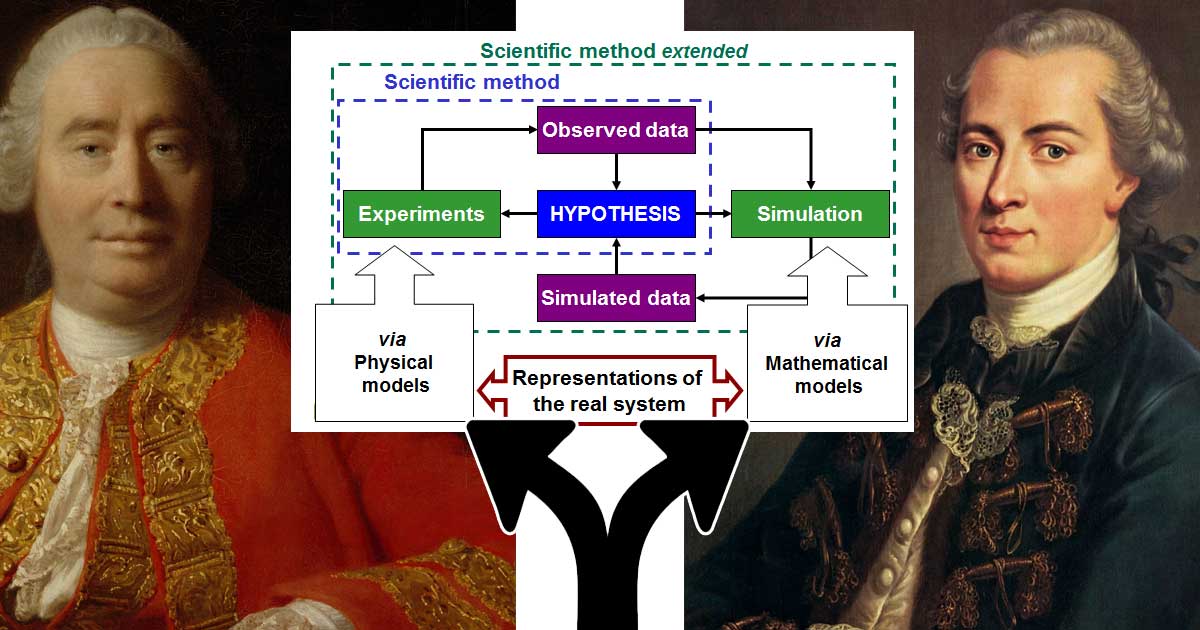
“Hume’s fork” describes how we refer to Kant’s critique of Hume, who separated knowledge into two types: facts based on ideas and facts based on experience.
Philosophy is the study of the natural and theoretical nature of knowledge, reality, existence, and being. Philosophy can broken down into categories based on subject and technique. See the branches of philosophy.

“Hume’s fork” describes how we refer to Kant’s critique of Hume, who separated knowledge into two types: facts based on ideas and facts based on experience.
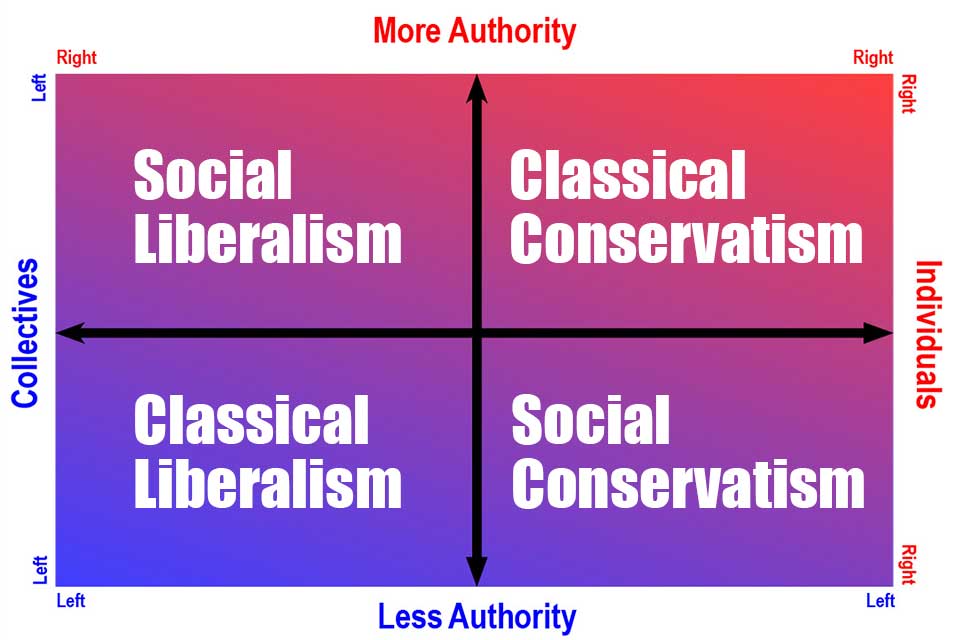
We explain liberalism and conservatism, including the different social and classical types of liberalism and conservatism.

Game theory involves games, but it isn’t the study of games. It is the study of mathematical models of conflict and cooperation regarding decision making.

Political realism is dealing with politics as they are in reality, political idealism is dealing with politics as an ideal.

Many (including Rousseau) consider Machiavelli’s The Prince to be satire, expressing a preference for a free republic over a hereditary principality.

For a given market, the choice always boils down to state intervention vs. the free-market, there is no third option (unless you count mixed-markets).

Niccolò Machiavelli can be considered the father of modern political science, and his book The Prince one of the first works of modern political philosophy (if not just modern philosophy).

We explore the nature of truth, the different types of truth, and the different types of entities who report truth to better understand the nature of information.
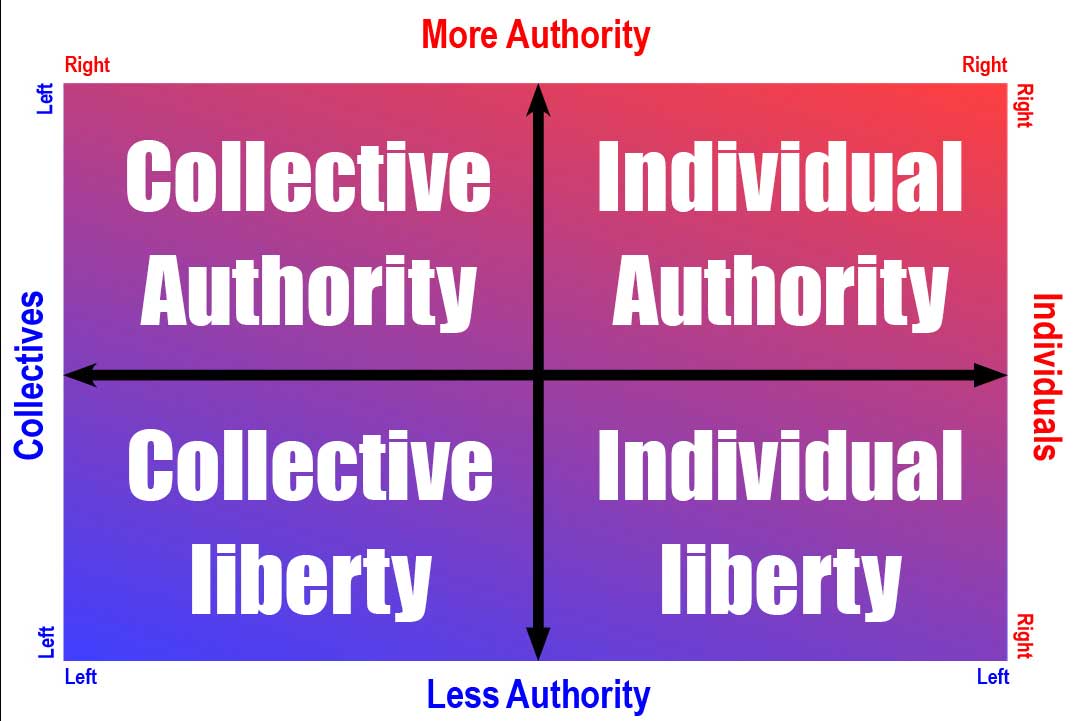
Collectivism describes ideology (political or otherwise) that favors the collective, like-wise Individualism describes ideology that favors the individual.
Here is a list of the fundamental dualities relating to human nature and the physical and conceptual universe.