What is Light?
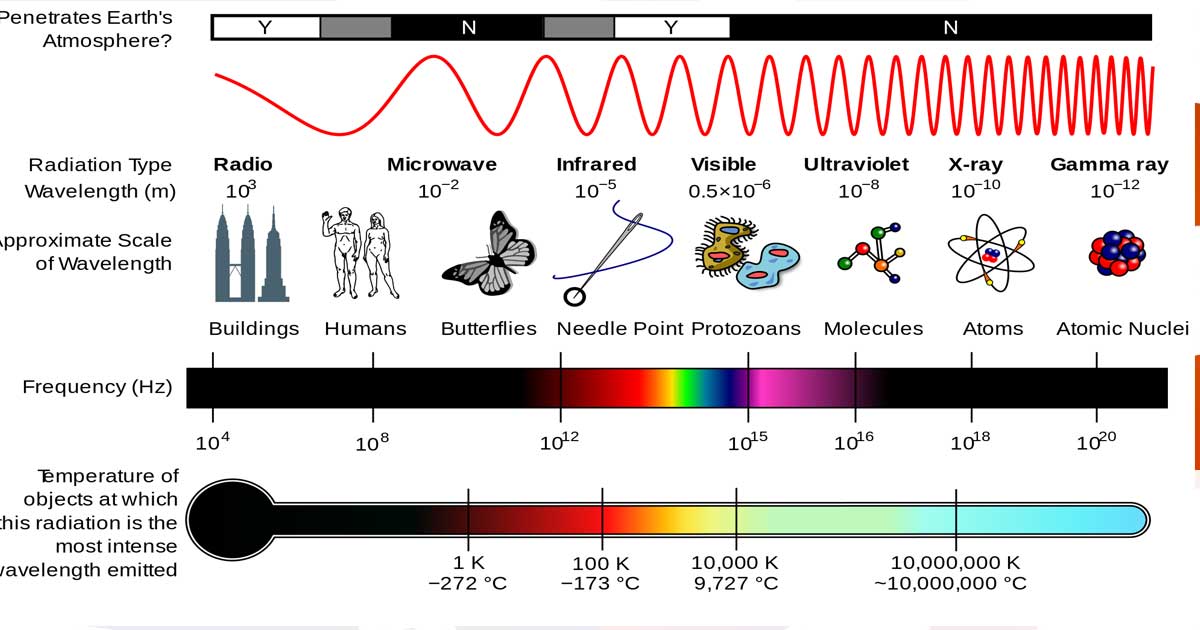
We explain “light,” both as electromagnetic radiation within a visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and as electromagnetic energy carried by photons.
Energy is the fundamental property of all objects in the universe. Energy can be transferred and transformed, but never created or destroyed.
Common forms of energy include: Kinetic energy of a moving object, the radiant energy carried by light, the potential energy stored by an object’s position in a force field (gravitational, electric or magnetic), elastic energy stored by stretching solid objects, chemical energy released when a fuel burns, and the thermal energy due to an object’s temperature.
Mass and energy are “equivalent” (mass-energy equivalence), but not exactly the same thing. Energy and mass can be converted into each other mathematically, and conserved as each other physically.
All things in the universe, especially living organisms and systems, require energy. A good example of how energy fuels the universe being that humans get energy from food (calories).

We explain “light,” both as electromagnetic radiation within a visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and as electromagnetic energy carried by photons.
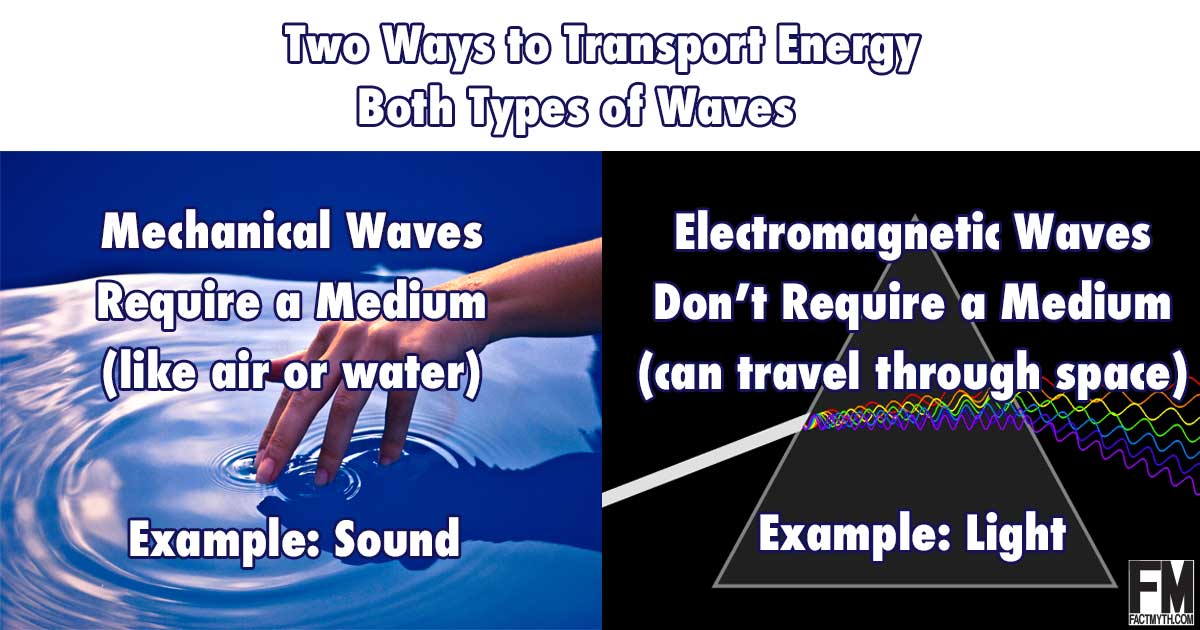
There are two types of waves: mechanical waves like sound that must travel through a medium like air, and electromagnetic waves like light that don’t.
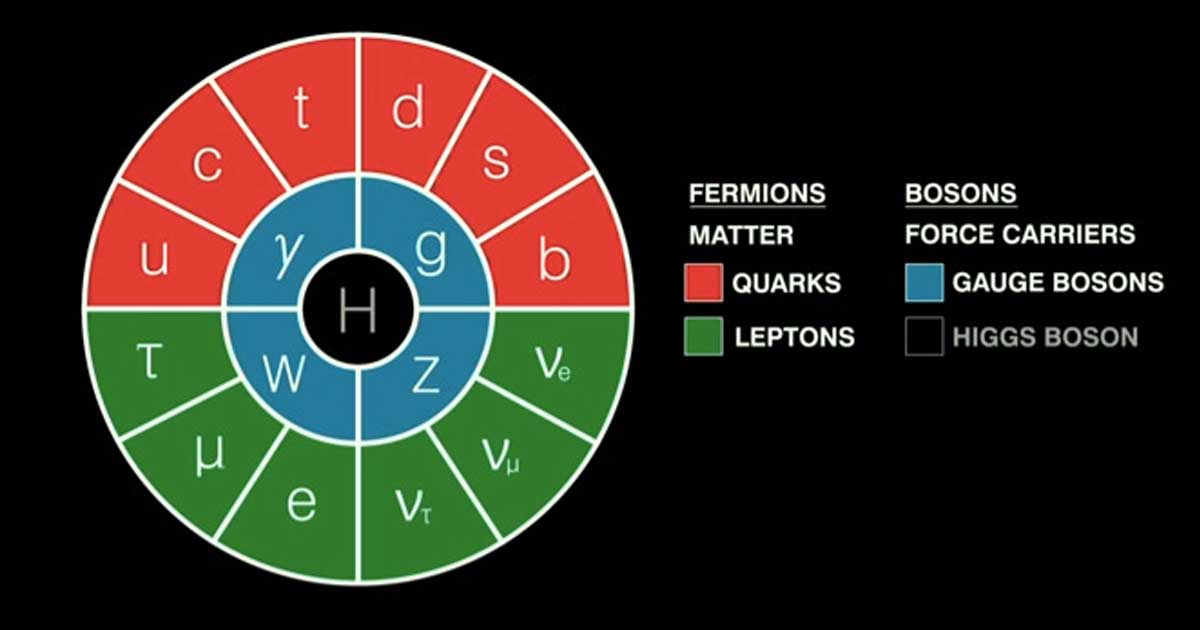
We explain the standard model of particle physics in simple terms for non-experts using videos, facts, and bullet points.