Political Ideology Simplified

Most political positions can be described using a limited set of political terms related to classical and social liberalism and conservatism.
Liberalism is the ideology of liberty and equality, conservatism is the ideology of authority, hierarchy, tradition, and order.
Liberalism is a political philosophy based on the principles of liberty and equality that grew out of the Age of Enlightenment.
If you don’t want the King or Church taking your life, liberty, and property, if instead you believe you have “the right” of “consent”… you might be a liberal.
Likewise, conservatism is the opposition philosophy of liberalism. It is the check that balances liberalism.
both liberalism and conservatism come in classical and social forms and speak to issues of state, social issues, and economics. In terms of economics there are also classical and social forms of liberal and conservative economics.
There are a number of different forms of liberalism and conservatism which each denote differing ideologies, but they generally all share core principles (like all liberal ideologies share basic liberal and left-wing planks and all conservative ideologies generally share basic conservative and right-wing planks).
With the above said:

Most political positions can be described using a limited set of political terms related to classical and social liberalism and conservatism.

Social Conservatism is the ideology of social hierarchy and tradition that mixes liberal and conservative views. It comes in political and economic forms.
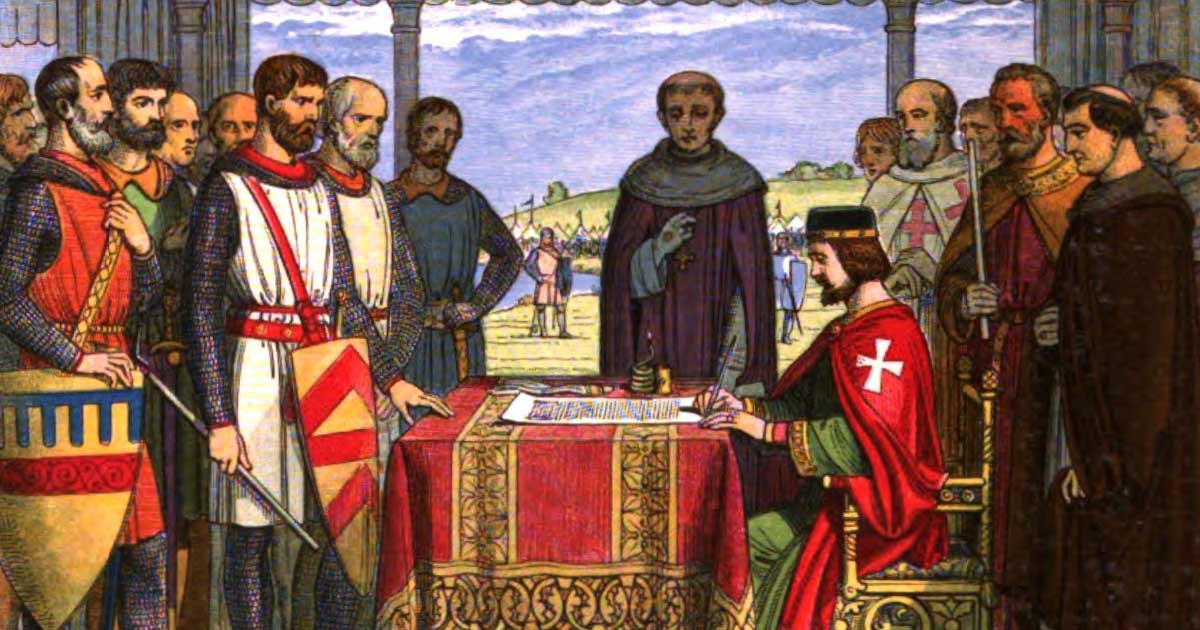

Classical Conservatism is the ideology of authority, hierarchy, order, and tradition (like classical aristocracy). It comes in political and economic forms.

Social liberalism is the ideology of collective liberties and rights that favors social welfare and justice. It comes in a political and economic form.

Classical liberalism is the ideology of liberties, rights, individualism, reason, and tolerance that comes in a political and economic form.
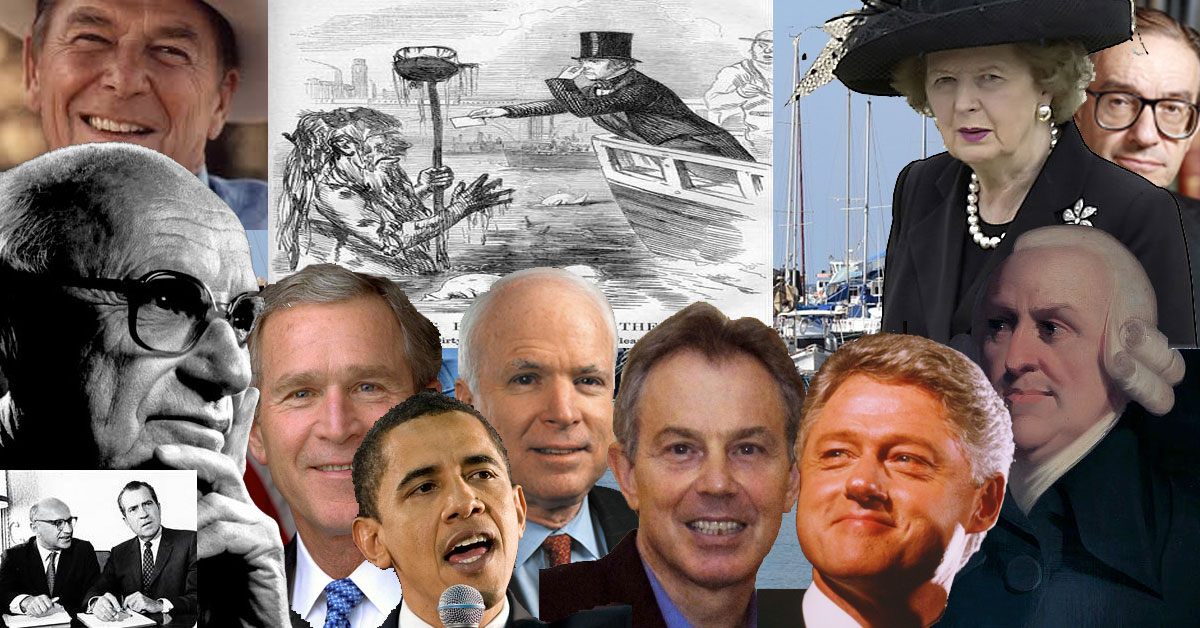

Neoliberalism is an economically-minded evolution of classical liberalism focused on deregulation, trade, and the private market. It is a “middle way” or “third way” between liberalism and conservatism.
Reason and logic are two closely related forms of thinking involving the comparison of terms that can be studied in terms of mathematics or philosophy and can be considered together as well as apart.
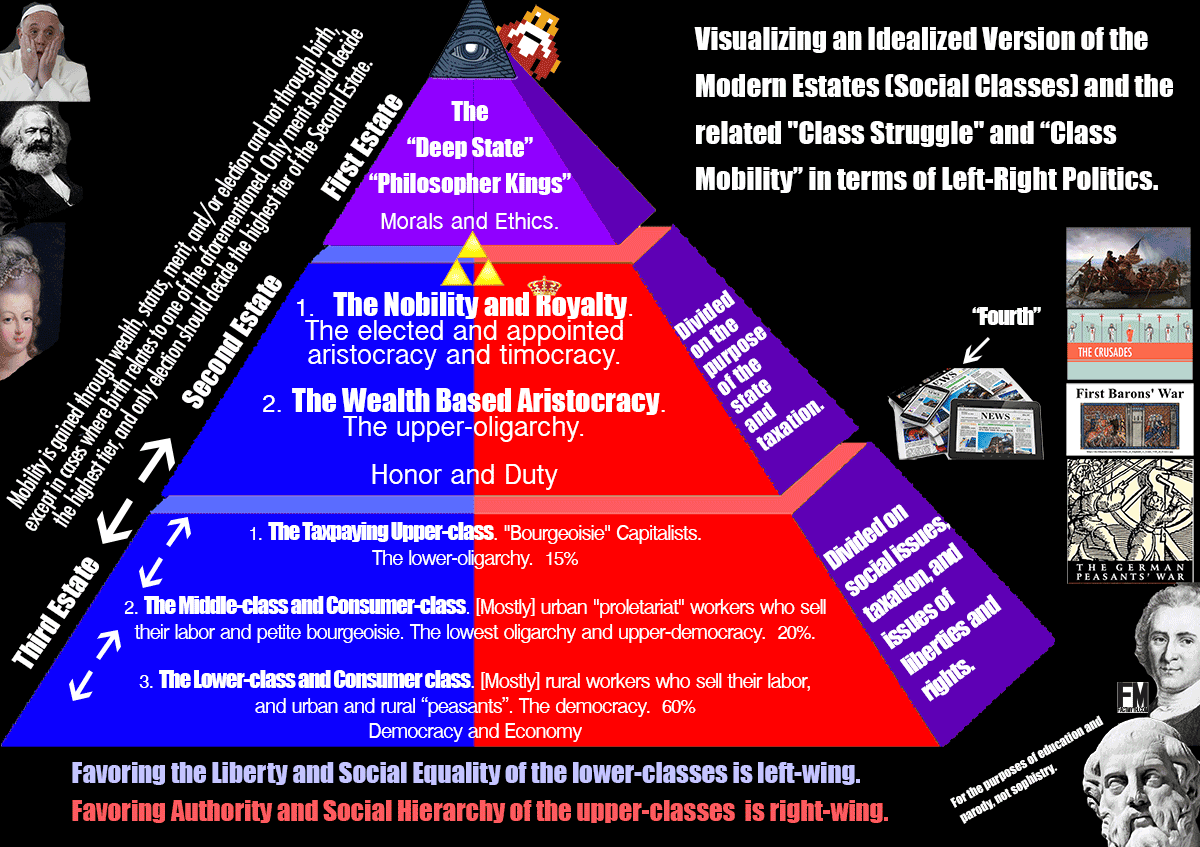
All nations have some sort of class system or class structure, generally based on wealth, birth, or status. We explain modern and historic social class systems and the general logic behind them to see to what extent they are natural and what extent they are convention.

We discuss the importance of individualism and the complexities involved in balancing the spirit of Individualism with collective responsibility.

Conservatism is the ideology of governmental, cultural, and economic order, tradition, hierarchy, and authority that generally comes in classical, social, and economic forms.