Understanding Marx and Marxian Class Theory

We present a simple guide to Marx, Marxian class theory, Marx’s theory of history, and Marx’s economic theories to help westerners understand what Marx was all about.
History is the study of the past and how it relates to the human experience.

We present a simple guide to Marx, Marxian class theory, Marx’s theory of history, and Marx’s economic theories to help westerners understand what Marx was all about.

Despite misconceptions, the United States is not a corporation. This can be confirmed by its lack of incorporating acts, its sovereign immunity, and past court cases, among other things.

Many past political, economic, and social philosophers were historians. This includes Locke, Hume, Keynes, Hegel, Ciciero, Marx, Mises, Aristotle, Kant, Smith, Plato, Machiavelli, Montesquieu, Engels, Rousseau, Hobbes, etc.

Despite two parties dominating politics due to a majority being needed to win elections, the United States doesn’t officially have a two-party system. Parties aren’t even mentioned in the Constitution.

While the term Columbia sometimes refers to the whole New World (all the Americas), historically the United States of America was referred to as Columbia.
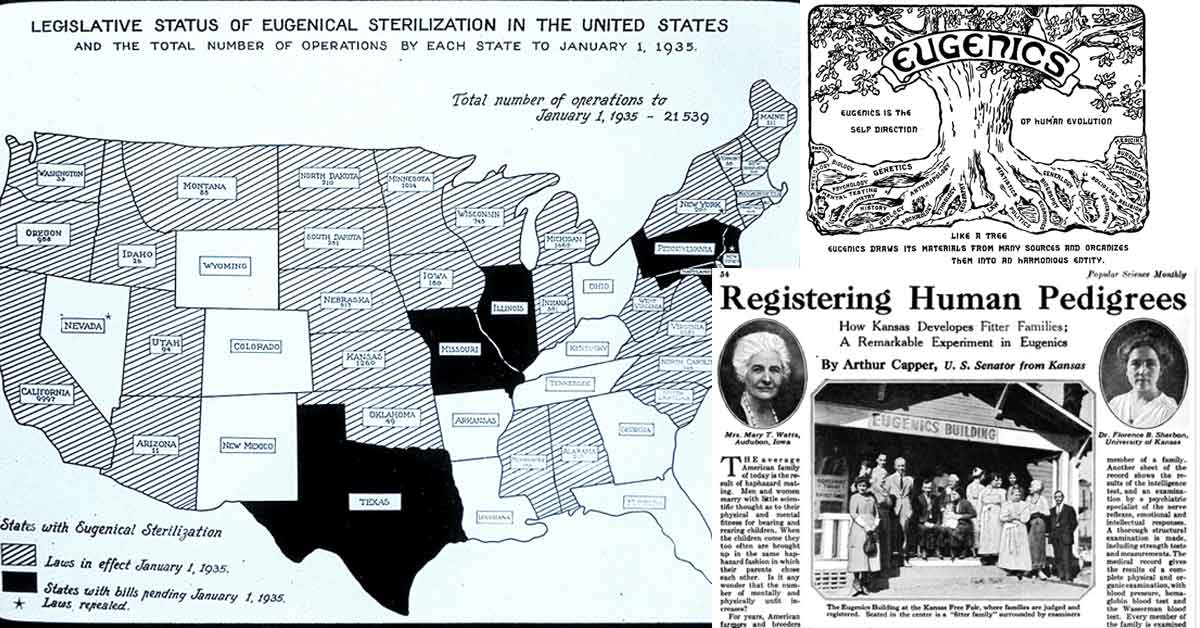
Eugenics (including positive eugenics which breeds traits, and negative eugenics which prevents breeding) has been practiced since the Greeks, but rose to popularity in the west starting in the late 1800’s.
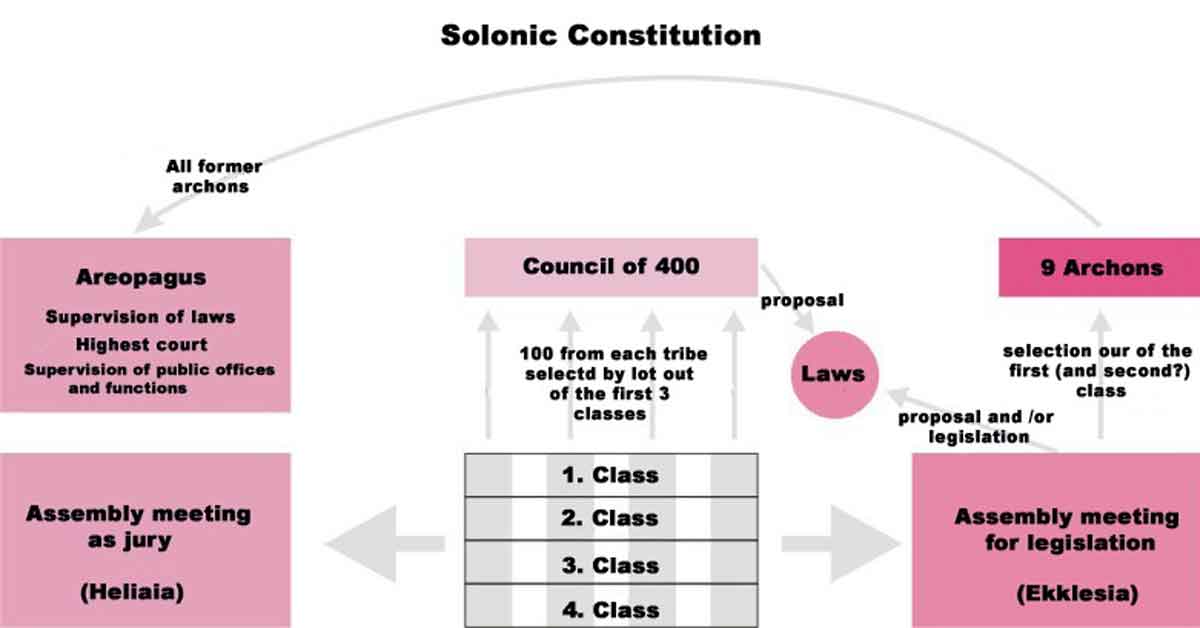
Classical Athens had a type of Direct Democracy that included direct voting on laws and election by lottery, but participation was limited to adult male citizens who owned land.

Sparta can be described as a constitutional nationalist socialist state with an oligarchical republican government where societal roles were based on hereditary class.

One might assume James Monroe wrote the 1823 Monroe Doctrine, but its primary author was future-President and then secretary-of-state John Quincy Adams.
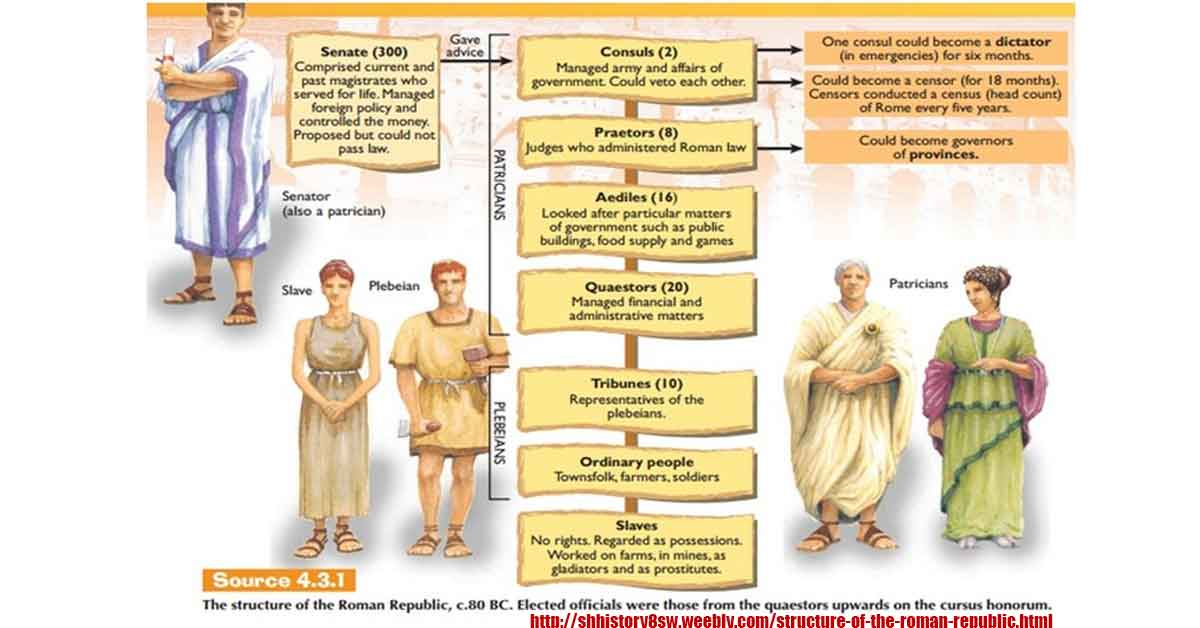
The Optimates like Pompey (aristocrats) and Populares like Julius Caesar (populists) were two opposing political factions at the onset of the fall of the Roman Republic.