Hillary Clinton Won the Popular Vote

Hillary Clinton won the national popular vote, but Donald Trump won the 2016 election by electoral vote due to the way the electoral college works.
Political Science is the science of politics, or the science of the nation-state. It is the art of diplomacy, the study of ideas, ideologies, and influence, the science of strategy, economics, and rhetoric, and more. Perhaps political science is best summed up by Aristotle in his discussing of man’s role in creating the ideal nation-city-state:
“Political science aims at what is the highest of all goods achievable by action…. though it is worth while to attain the end [AKA happiness/arete/”the greatest good”/”the highest good”] merely for one man, it is finer and more godlike to attain it for a nation or for city-states. These, then, are the ends at which our inquiry aims, since it is political science, in one sense of that term.” – Aristotle on the meaning of life, virtue, morals, ethics, and the city-state, Nicomachean Ethics 350 BC

Hillary Clinton won the national popular vote, but Donald Trump won the 2016 election by electoral vote due to the way the electoral college works.
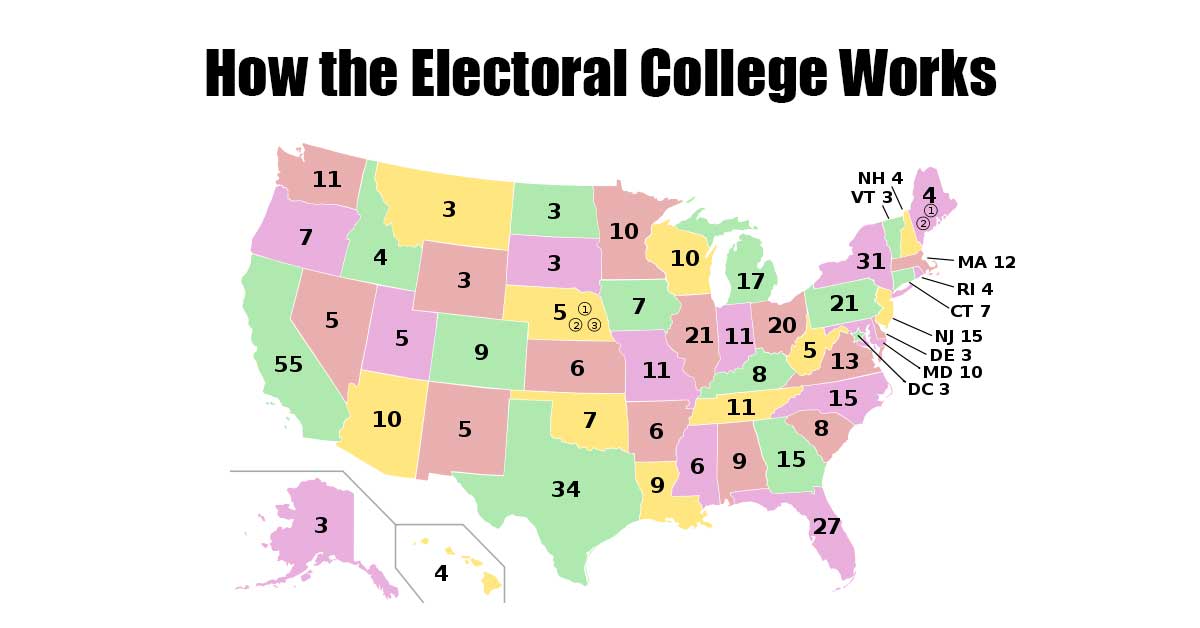
In the U.S., the President and Vice President are elected by getting a majority of electoral college votes, they are not elected by popular vote.

If the 2016 election proved anything, it proved that the votes of progressive populists (like Bernie) and nativist populists (like Trump) matter in elections.

We explain Guy Fawkes, Guy Fawkes Day, and the symbolism behind the the Guy Fawkes mask, the fifth of November, and the Gunpowder, Treason, and Plot.

We present a simple guide to Marx, Marxian class theory, Marx’s theory of history, and Marx’s economic theories to help westerners understand what Marx was all about.

Civil War, Revolution, and Rebellion all refer to different types of disputes between citizens of country regarding governmental power or authority.

Despite misconceptions, the United States is not a corporation. This can be confirmed by its lack of incorporating acts, its sovereign immunity, and past court cases, among other things.

John Locke can be considered the father of liberalism. His theories on life, liberty, property, consent, and the social contract form the foundation of classical liberalism.

“Civil Religion” is the civic “religion” of a nation. It doesn’t describe the theological religion of a nation, but rather a quasi-religious shared identity built around national symbolism and customs.
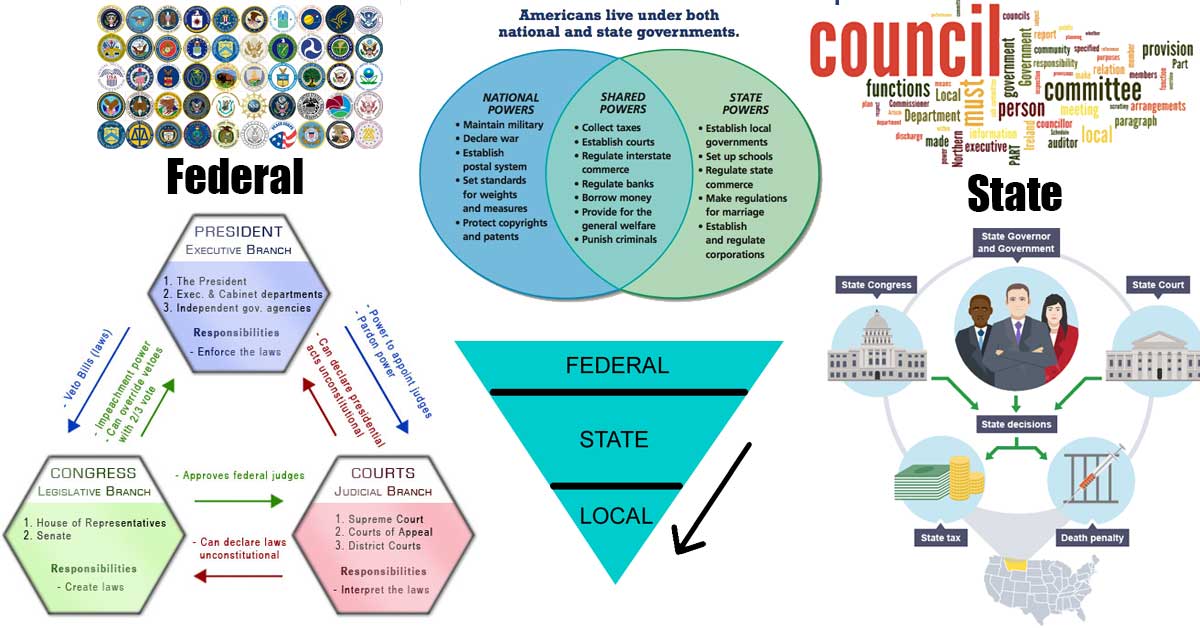
Separation of Powers describes the way in which government is divided into different branches (ex. in the U.S., the legislative, executive, and judicial). Checks and balances describe the powers each branch has to “check” the other branches and ensure a balance of power.