Political Duopolies
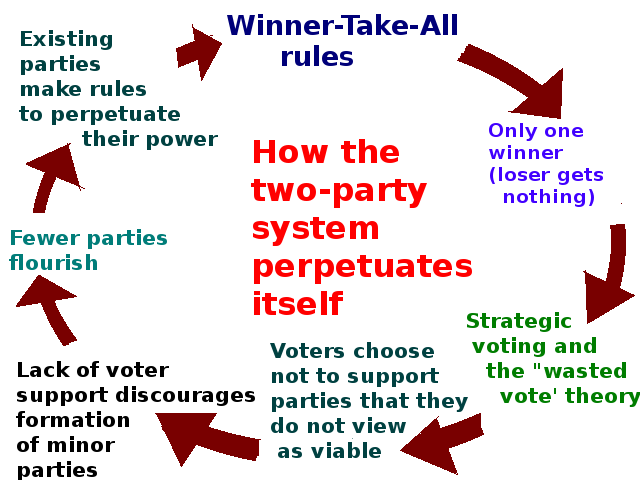
We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.
The political terms left and right are comparative terms that describe political views as: liberalism, collectivism, and liberty (left) vs. conservatism, individualism, and authority (right).
Since political ideology is a complex spectrum of beliefs and actions, the terms are best applied with nuance. They can be used to make absolute statements like Monarchies are right-wing forms of government in terms of power structure. Or they can be used to make comparative statements such as, a progressive Democrat is to the right of a radical anarchist. See the pages below for detailed discussions into the aspects of the political left and right.

We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.
In modern history political factions have often been represented by a color, we look at political color to understand color politics.

We explain neoliberalism, globalization, nativism, and protectionism and the pros and cons of “neoliberal globalization” and “nativist protectionism.”
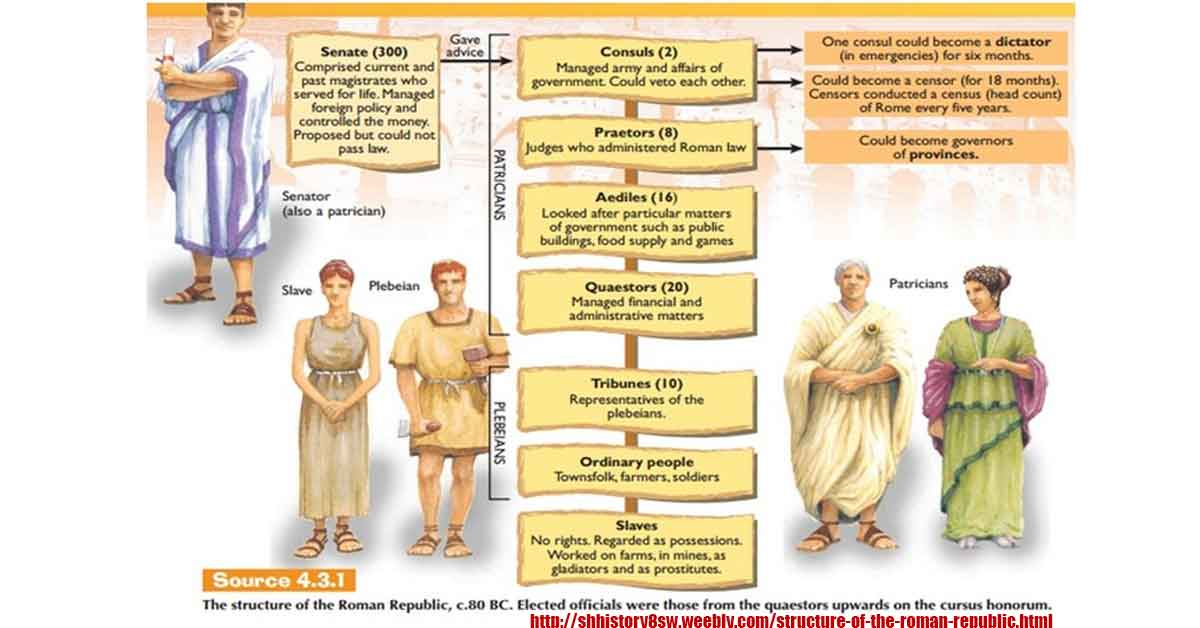
The Optimates like Pompey (aristocrats) and Populares like Julius Caesar (populists) were two opposing political factions at the onset of the fall of the Roman Republic.
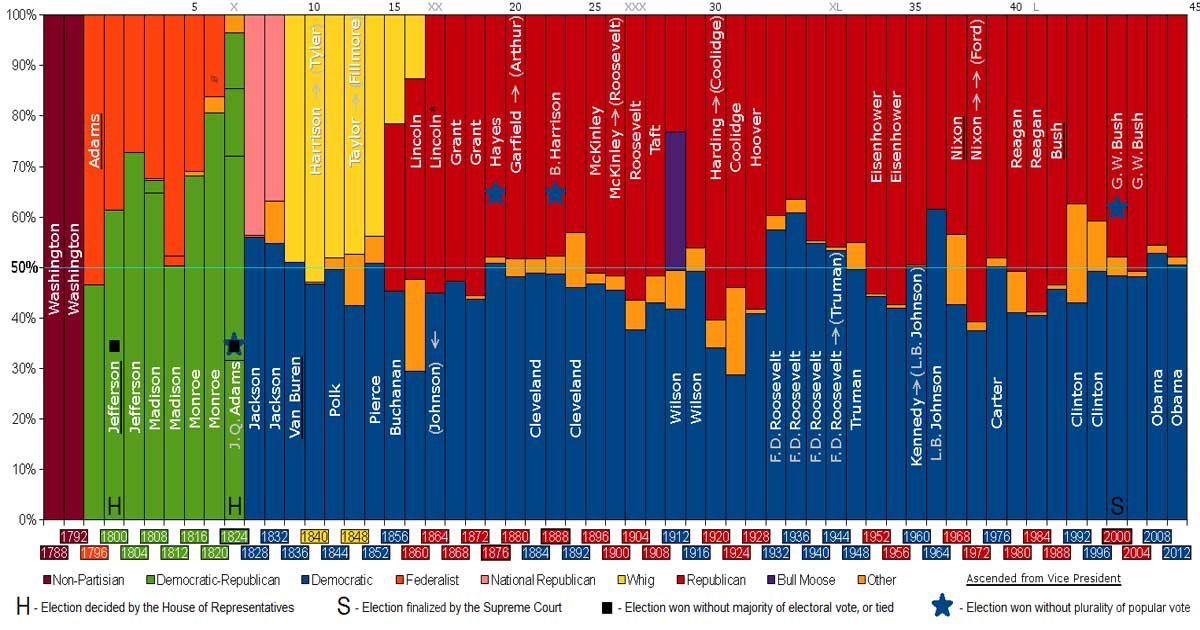
We list the U.S. Presidents, their political parties, and their political ideologies alongside descriptions of their Presidency to examine U.S. history.
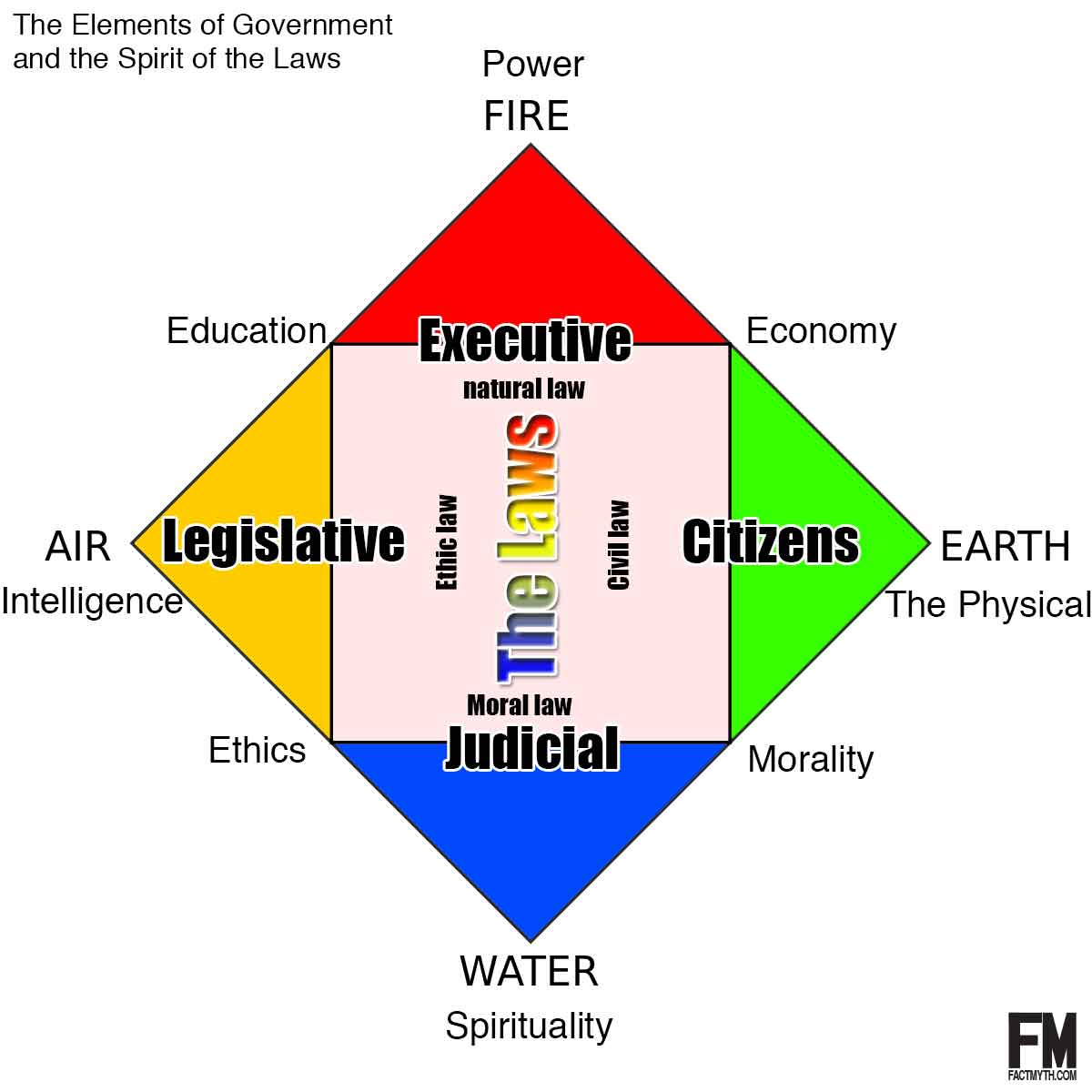
The four “elements” (or “powers”) that form the foundation of government can roughly be expressed as: citizens, executive, legislative, and judicial.

Modern banking originated in Italy around 1150 as Jews fleeing persecution brought new practices, including “discounting”, to the merchant banks of the Italian piazzas.

Below we present an annotated version of Andrew Carnegie’s 1889 essay Wealth (better known as the Gospel of Wealth).

The state of nature is the state humans lived in before forming the first societies. By examining the state of nature we can better understand the implicit and explicit social contracts which govern societies.

Different types of government can be said to be based on a number of attributes like power source, power structure, and economic system.