Political Duopolies
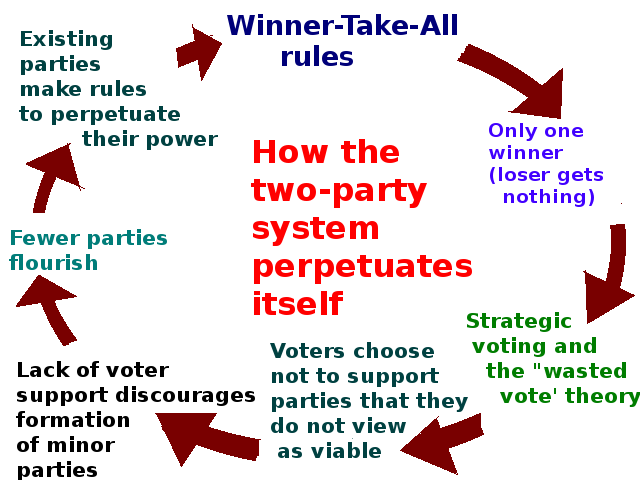
We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.
Liberalism is the ideology of liberty and equality, conservatism is the ideology of authority, hierarchy, tradition, and order.
Liberalism is a political philosophy based on the principles of liberty and equality that grew out of the Age of Enlightenment.
If you don’t want the King or Church taking your life, liberty, and property, if instead you believe you have “the right” of “consent”… you might be a liberal.
Likewise, conservatism is the opposition philosophy of liberalism. It is the check that balances liberalism.
both liberalism and conservatism come in classical and social forms and speak to issues of state, social issues, and economics. In terms of economics there are also classical and social forms of liberal and conservative economics.
There are a number of different forms of liberalism and conservatism which each denote differing ideologies, but they generally all share core principles (like all liberal ideologies share basic liberal and left-wing planks and all conservative ideologies generally share basic conservative and right-wing planks).
With the above said:

We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.

We explain neoliberalism, globalization, nativism, and protectionism and the pros and cons of “neoliberal globalization” and “nativist protectionism.”

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.
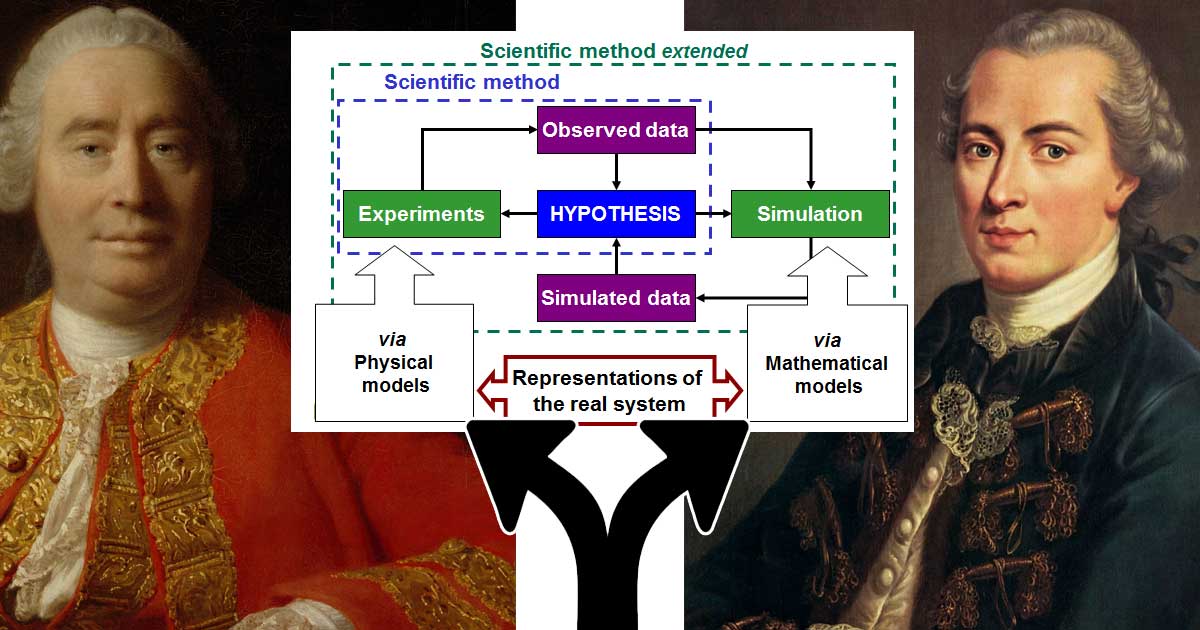
“Hume’s fork” describes how we refer to Kant’s critique of Hume, who separated knowledge into two types: facts based on ideas and facts based on experience.
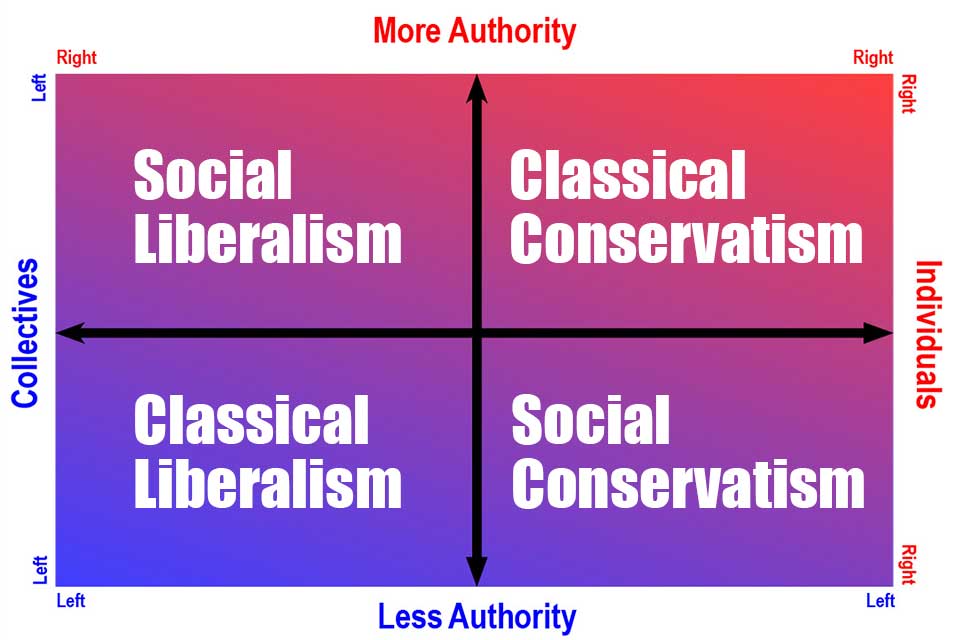
We explain liberalism and conservatism, including the different social and classical types of liberalism and conservatism.

We explain the political terms conservative, moderate, liberal, progressive, and radical and how they are used in different contexts.
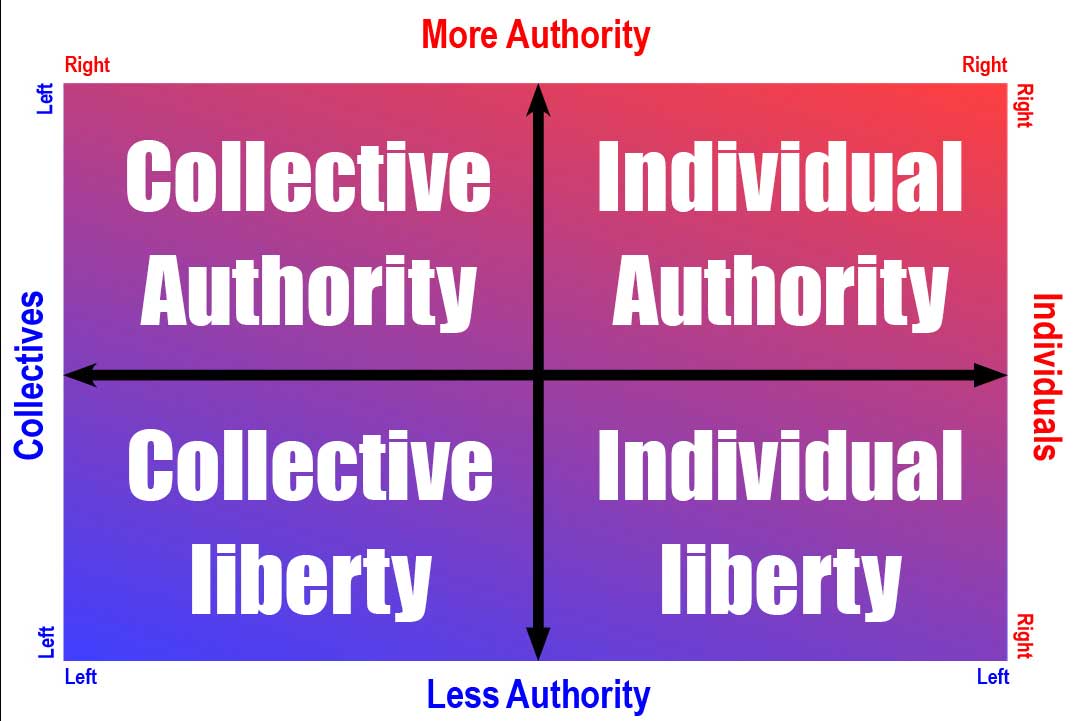
Collectivism describes ideology (political or otherwise) that favors the collective, like-wise Individualism describes ideology that favors the individual.
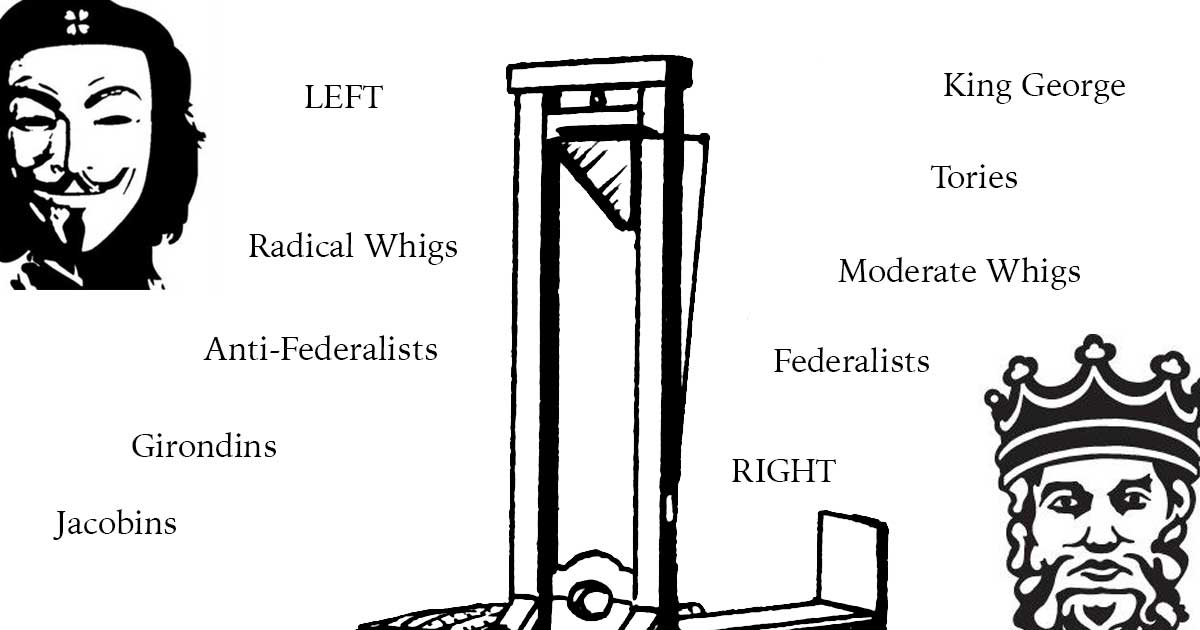
The modern usage of the political terms left and right comes from the French Revolution of 1789 when supporters of the king stood to the president’s right, and supporters of the revolution to his left.

Classical liberalism arose in opposition to state-imposed religion and aristocracy in the 1600 – 1700’s during the Age of Enlightenment in Europe and America.

The United States is a Federal Republic with democratic values that some claim contains a growing oligarchy (or corporatocracy). We look at those claims.