Political Ideology Simplified

Most political positions can be described using a limited set of political terms related to classical and social liberalism and conservatism.

Most political positions can be described using a limited set of political terms related to classical and social liberalism and conservatism.

Social Conservatism is the ideology of social hierarchy and tradition that mixes liberal and conservative views. It comes in political and economic forms.
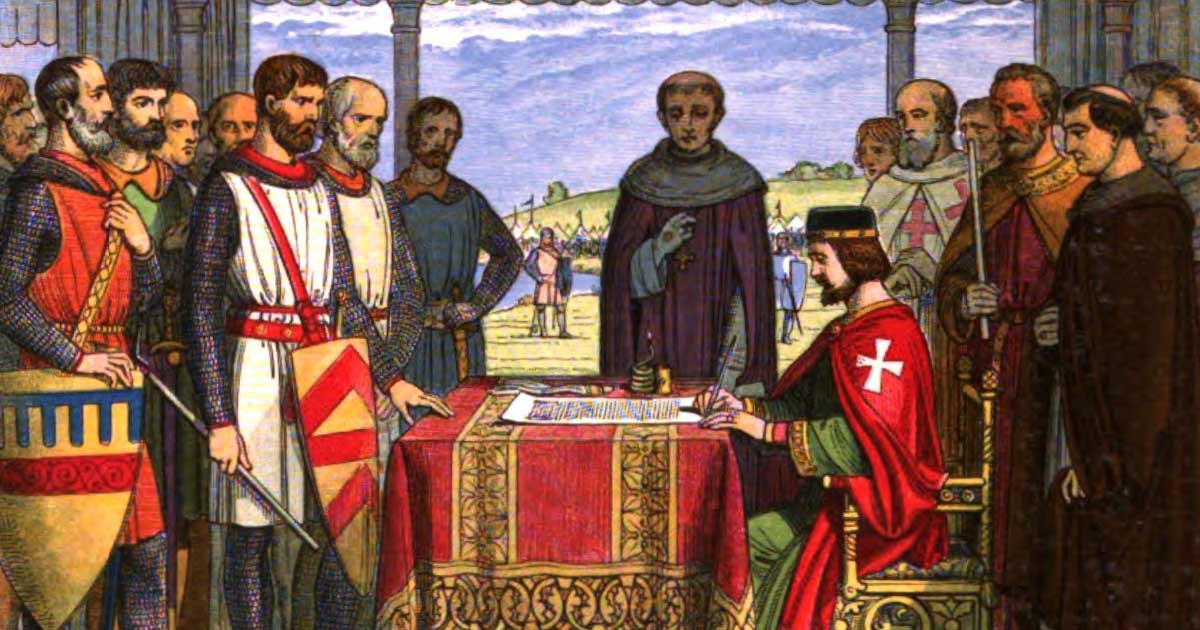

Classical Conservatism is the ideology of authority, hierarchy, order, and tradition (like classical aristocracy). It comes in political and economic forms.

Social liberalism is the ideology of collective liberties and rights that favors social welfare and justice. It comes in a political and economic form.

Classical liberalism is the ideology of liberties, rights, individualism, reason, and tolerance that comes in a political and economic form.

In simple terms, analysis examines a system by dividing a whole into its parts, and synthesis examines a system by combining and comparing parts.
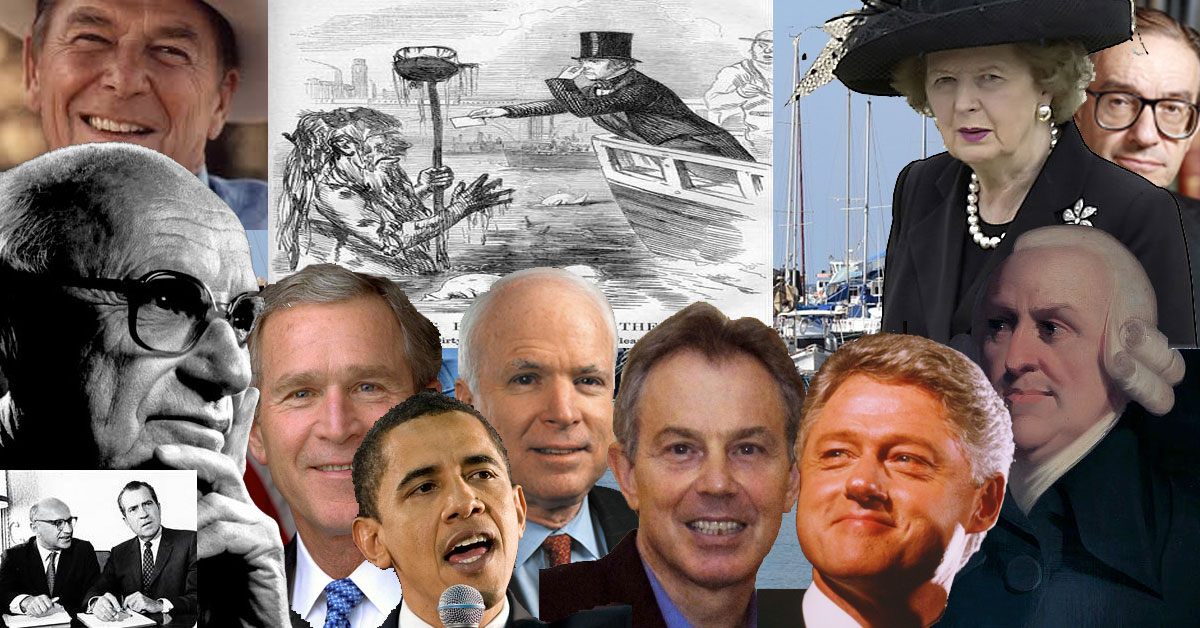

Neoliberalism is an economically-minded evolution of classical liberalism focused on deregulation, trade, and the private market. It is a “middle way” or “third way” between liberalism and conservatism.
We explain inductive reasoning, a bottom-up reasoning method that reasons by consistency, comparing particulars and probabilities to find likely truths.
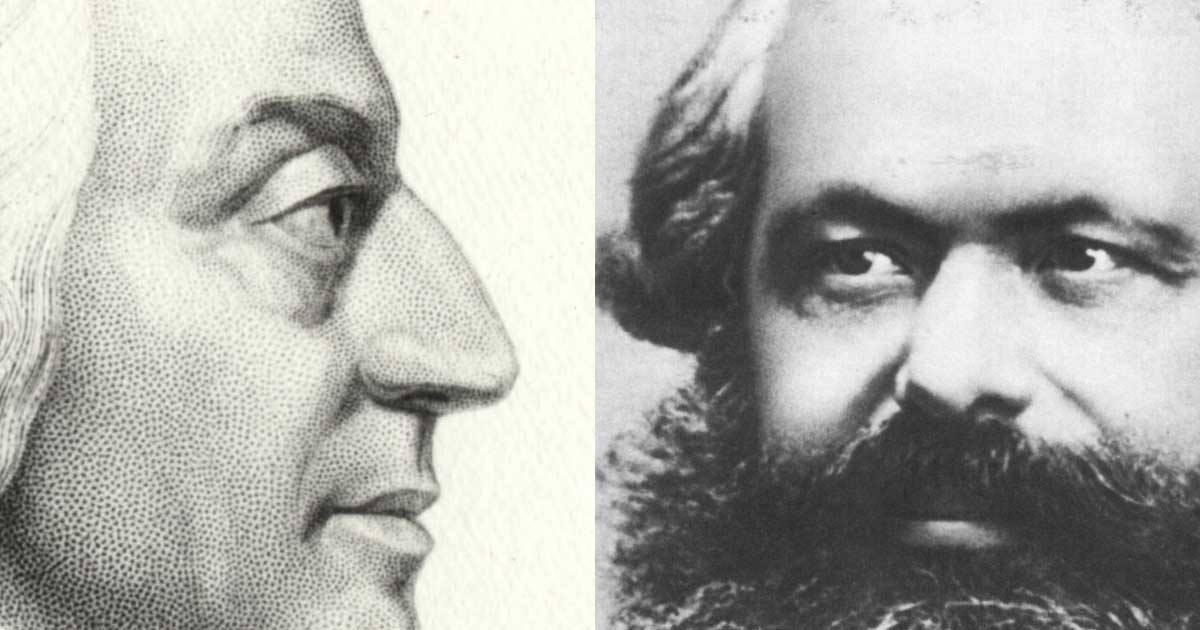

Labor and capital are economic terms that describe 1. workers and their labor power and, 2. capitalists and their material and financial capital.
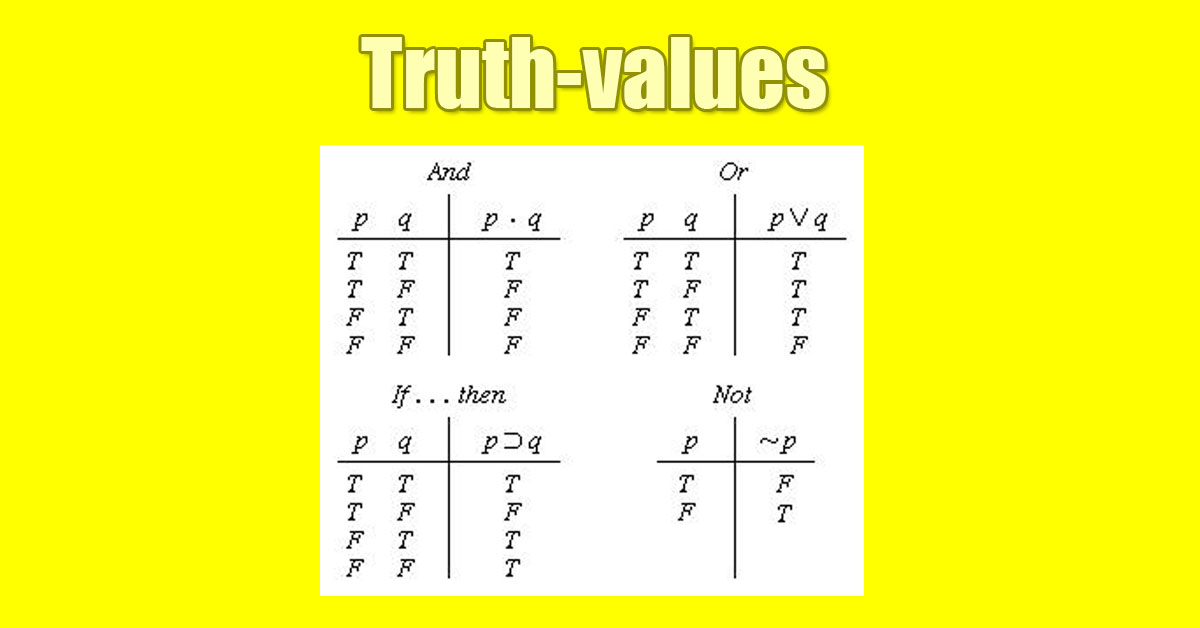
A truth-value is a label that is given to a statement (a proposition) that denotes the relation of the statement to truth.