Life is all About “Trade-offs”

Life is all about “trade-offs,” and almost everything in life is a trade-off. If one thing increases, another must decrease.
Philosophical theories are theories that are philosophical, rather than purely scientific by nature. Meanwhile, philosophical concepts can be loosely describes as ideas or “concepts” that are philosophical in nature.
Generally, a concept is a single idea, a theory is an explanation of how something works, and philosophy is simply the study of that which we can’t know for sure (see the branches of philosophy.).
So then, for our purposes, philosophical theories and concepts is simply a broad category that contains all non-scientific theories worth discussing.
TIP: For a great explainer on the basics of Philosophy see Tamar Gendler: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Politics and Economics by Big Think.
NOTE: Some scientific theories that spark metaphysical philosophical questions are categorized here (as well as under their respective scientific fields). Learn more about scientific theories.

Life is all about “trade-offs,” and almost everything in life is a trade-off. If one thing increases, another must decrease.
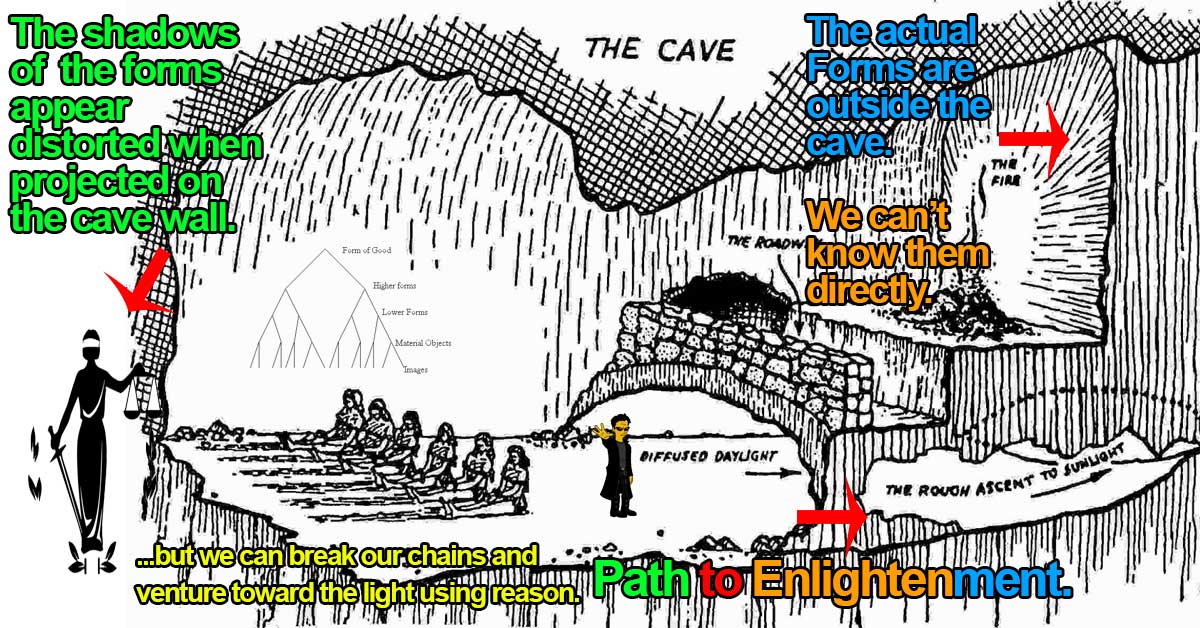
We explain Plato’s Allegory of the Cave and Plato’s Theory of the Forms to help readers understand the essence of Plato’s overarching theory.

No one knows what it is like before or after death, but logically, after you die will be like before you were born.

Political emotion is a term that describes emotional attachments and responses to political ideas and responses to political ideas based on emotion.

Progressive Centrism, often known as “Radical Centrism”, is center-wing centrism (a balanced left-right ideology) that is progressive (wants change quickly).

Identity Politics describes identifying with a concept, or being perceived as identifying with a concept, and the social and political implications of that.
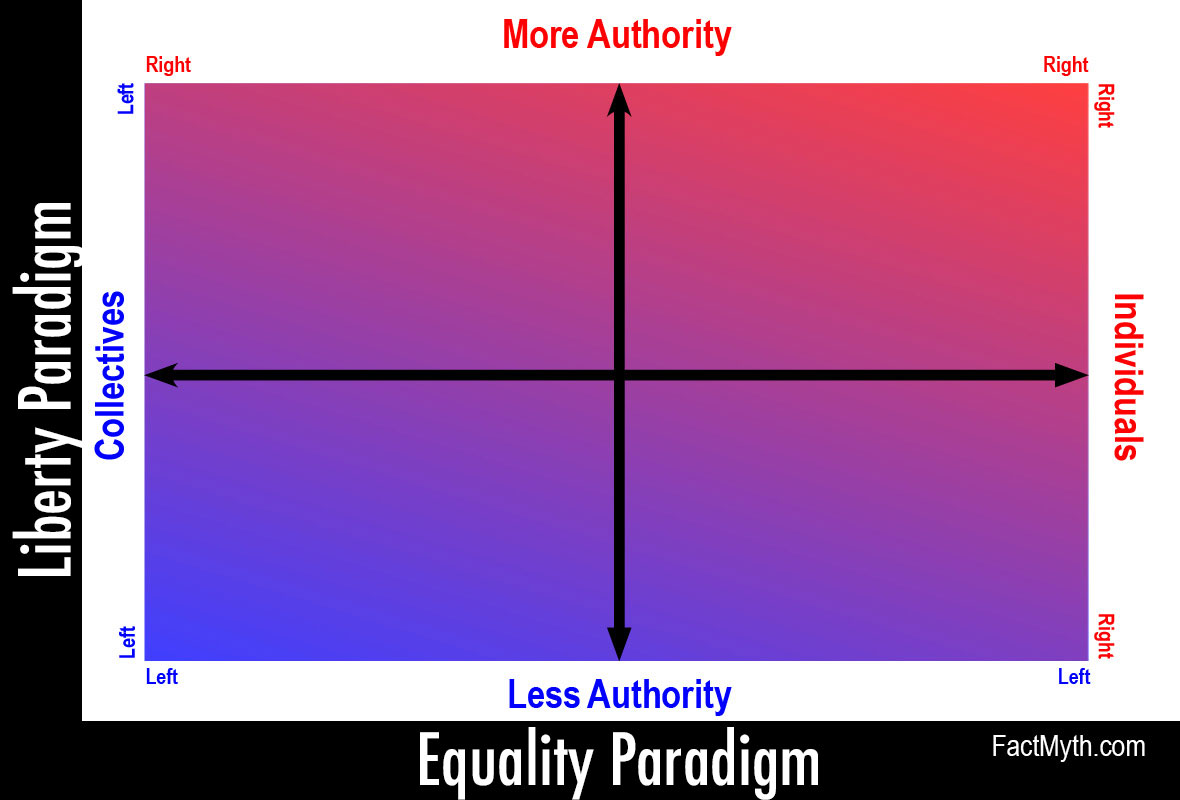
We describe a “purple strategy” modeled off purple state politics, for the Defense of Western Liberal Democracy and Republicanism.

We discuss theories that deal with the nature of abstractions and contradictions including, Dialectics and the Golden Mean theory, and offer a “synthesis” of these theories.
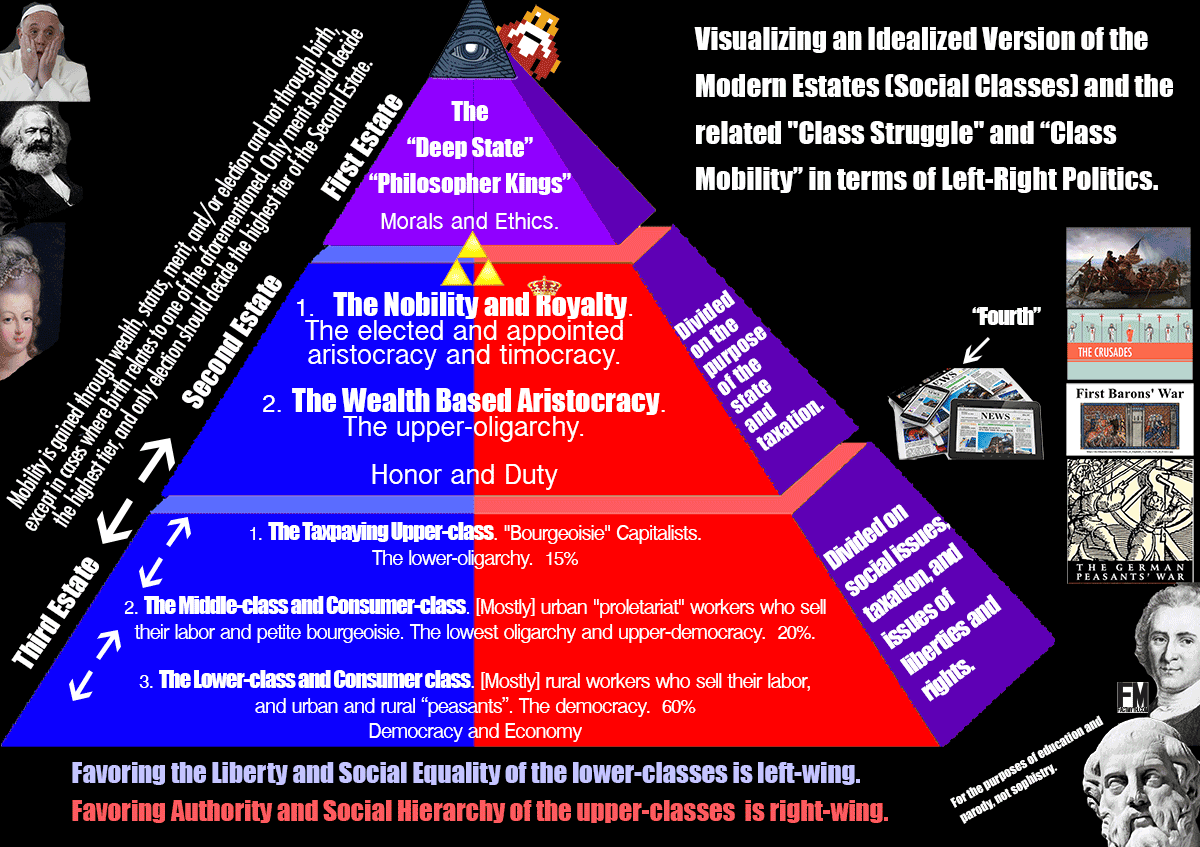
All nations have some sort of class system or class structure, generally based on wealth, birth, or status. We explain modern and historic social class systems and the general logic behind them to see to what extent they are natural and what extent they are convention.

We discuss the importance of individualism and the complexities involved in balancing the spirit of Individualism with collective responsibility.