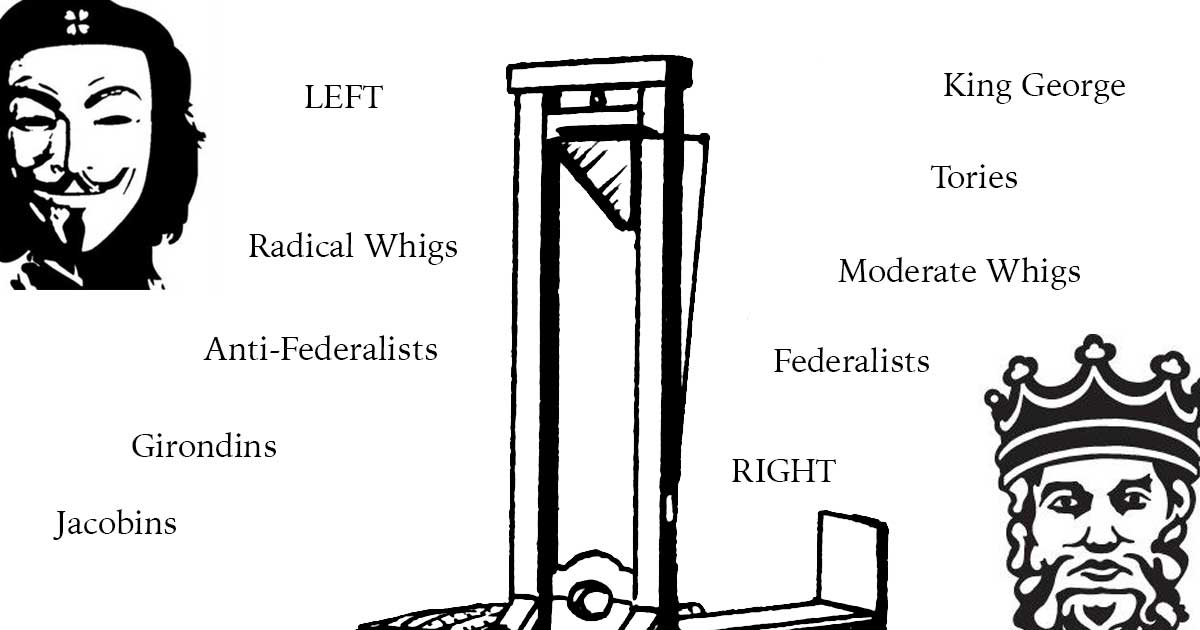
Understanding Populism
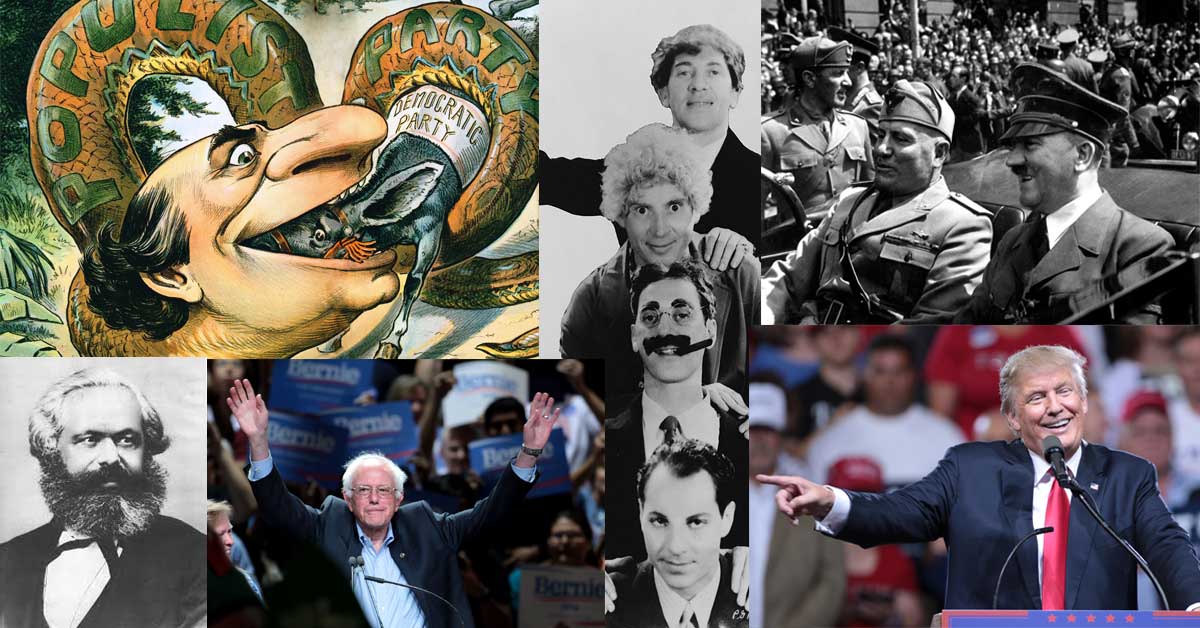

Populism is a broad term that generally describes popular sentiment felt by the working class against the elites. It can look like social conservative nativist right-wing populism or social liberal progressive left-wing populism.