France, officially the French Republic, is a sovereign state including territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean.
During the Iron Age, what is now Metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The Gauls were conquered in 51 BC by the Roman Empire, which held Gaul until 486. The Gallo-Romans were superseded by the Germanic Franks, who formed the medieval Kingdom of France. France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years’ War (1337 to 1453) strengthening state-building and the political centralization. During the Renaissance, France experienced a vast cultural development and established the beginning of a global colonial empire. The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
France became Europe’s dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV. Later, during the end of the 1700’s the French Revolution resulted in “liberty”, shortly after Napoleon took over. After Napoleon’s defeat France became a constitutional monarchy in 1830 and has since went through a series of republics. – From Wikipedia.

Populism is a broad term that generally describes popular sentiment felt by the working class against the elites. It can look like social conservative nativist right-wing populism or social liberal progressive left-wing populism.

We examine the historical effects of social, political, and economic inequality on society to see how it has led to social unrest and events like revolutions and populist uprisings.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.

We explain the political terms conservative, moderate, liberal, progressive, and radical and how they are used in different contexts.
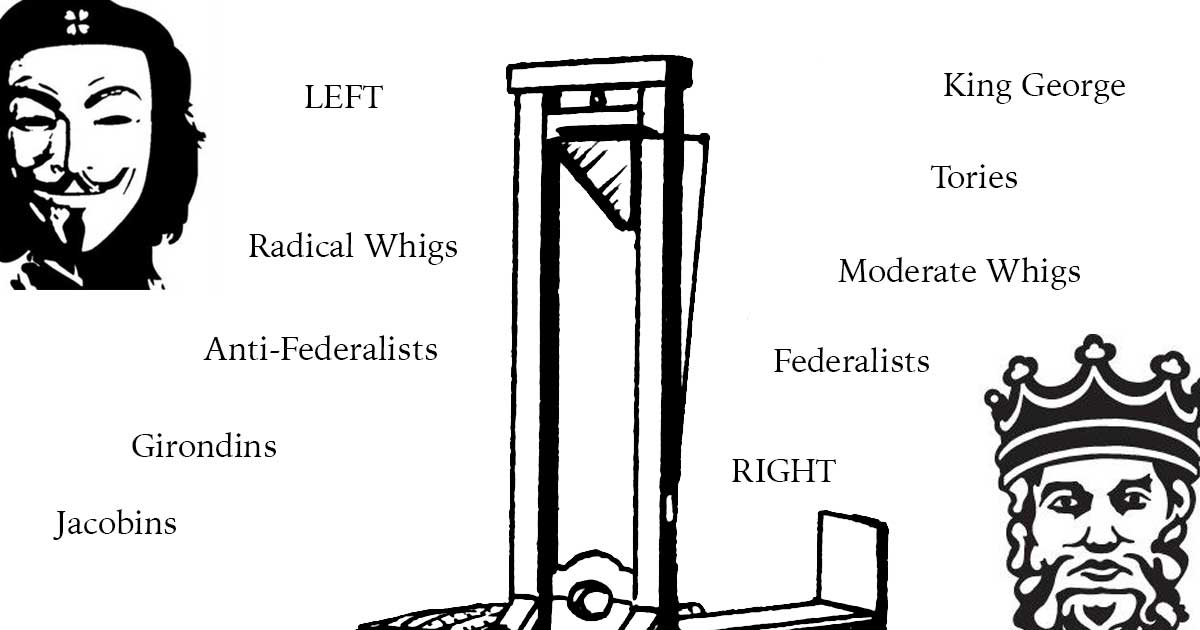
The modern usage of the political terms left and right comes from the French Revolution of 1789 when supporters of the king stood to the president’s right, and supporters of the revolution to his left.

We present a summary of the history of human rights documents including the Bill of Rights, Magna Carta, Declaration of Rights and Man, and English Bill of Rights.

Classical liberalism arose in opposition to state-imposed religion and aristocracy in the 1600 – 1700’s during the Age of Enlightenment in Europe and America.







