What is Classical Liberalism?

Classical liberalism is the ideology of liberties, rights, individualism, reason, and tolerance that comes in a political and economic form.
John Locke is arguably the father of liberalism. Considering that western democracy is founded on liberalism, this makes him one of the most important thinkers of all time.
John Locke’s ideas include the right to life, liberty, and the ownership of property, the right to not be owned as a slave, the non-aggression principle, the state of nature, and the social contract. Other important thinkers from Locke’s time include Hobbes and Voltaire.
His most notable work is his Second Treatise of Government. This book contains almost all the principles that America is founded on, and was largely the ideological backbone of the England’s Glorious revolution and the French revolution.

Classical liberalism is the ideology of liberties, rights, individualism, reason, and tolerance that comes in a political and economic form.

We often attribute the origin of the state of nature argument to Hobbes, but it can be traced to thinkers like Plato, Aristotle, and the Sophists in the 300s BC, and is then mused on by other early philosophers.

Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government.
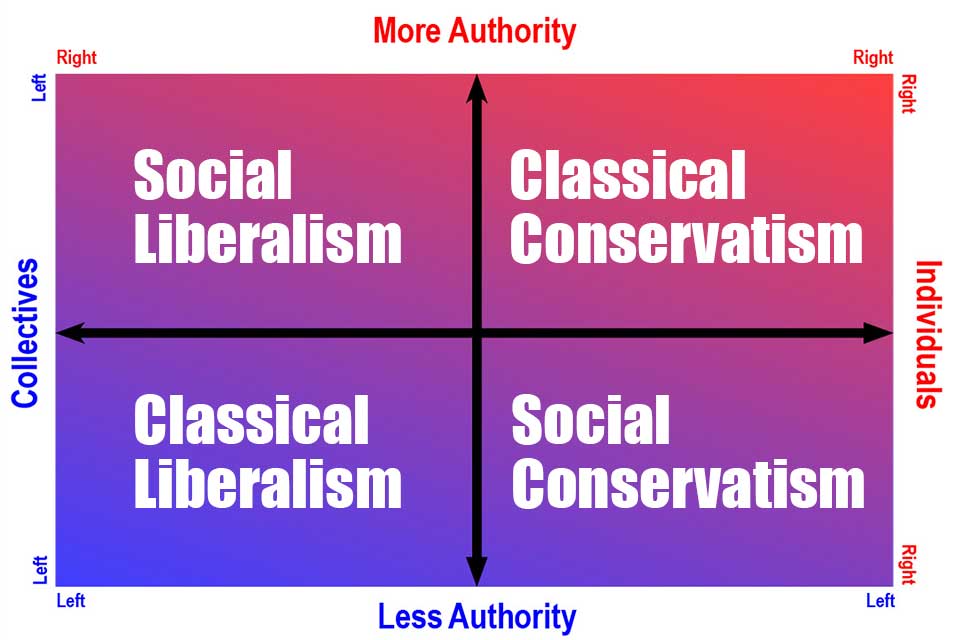
We explain liberalism and conservatism, including the different social and classical types of liberalism and conservatism.
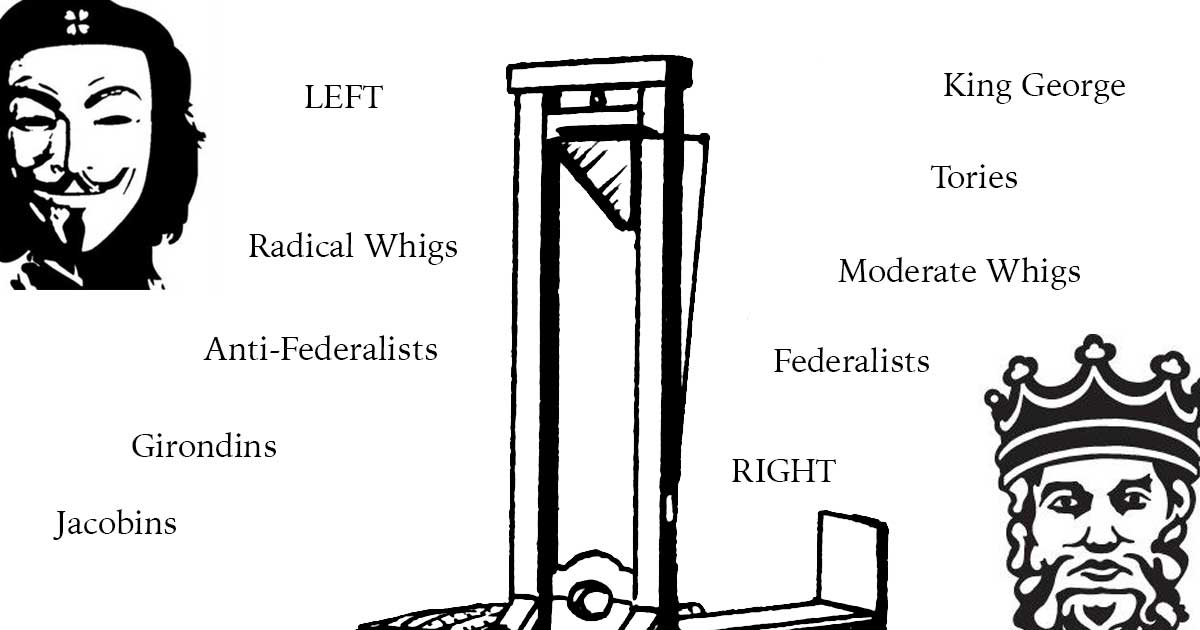
The modern usage of the political terms left and right comes from the French Revolution of 1789 when supporters of the king stood to the president’s right, and supporters of the revolution to his left.

Isaac Newton produced many well-known works in math, astronomy, and physics, but he produced about as many unpublished works which dealt with theology, alchemy, and the occult.

We present a summary of the history of human rights documents including the Bill of Rights, Magna Carta, Declaration of Rights and Man, and English Bill of Rights.

Classical liberalism arose in opposition to state-imposed religion and aristocracy in the 1600 – 1700’s during the Age of Enlightenment in Europe and America.
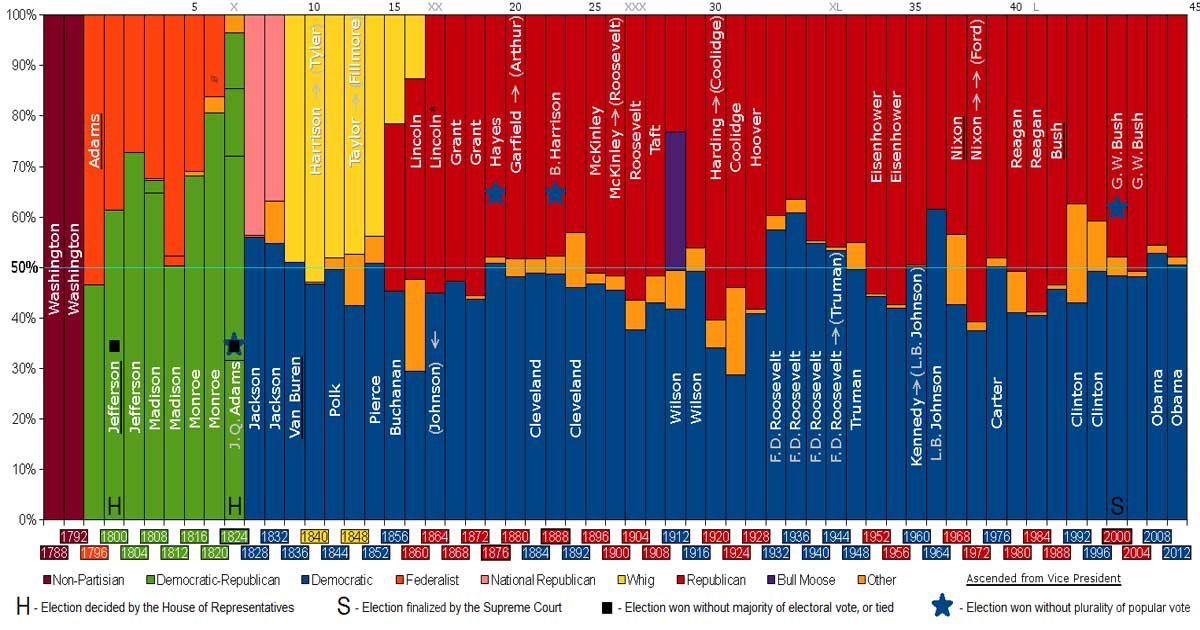
On this page, we look at political parties from a historical perspective to better understand the underlying left-right politics all political parties are based on.