What is the General Will?

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.
In politics and philosophy liberty refers to the civil freedoms to which all people are entitled, in a state of nature it refers to total freedom. Given this we can say there are generally two types of liberty:
Liber in Latin means free, so Liberty broadly refers to the idea that all humans are born with inalienable rights (rather than these rights being bestowed upon them by a Government). The political philosophy born from the concept of liberty is “liberalism” (with conservatism being the push against this). See Hobbes, Locke, Hume, Burke, and Mill. The political philosophy that came after this addressed additional civil liberties necessary for a just state, and this is called social liberalism.
Although there is no agreement on the definition of Liberty (see nearly every political faction and war fought from 1688 on), we can broadly say liberty includes concepts such as: the social contract, freedom from kings, freedom of speech, religion, press, and assembly, freedom of trade, and generally the freedom to consent to be governed. Or perhaps, in sum, simply the freedom to pursue happiness.
The Romanticist version sees all men as naturally good and applies liberty to emotions, libertines apply it to the freedom to enjoy life’s sensual pleasure, libertarians accept social injustice in exchange for individual liberty, social liberals say humans can’t have liberty if they live in squalor, some think democracy breeds liberty, others think it can only be obtained in a republic ruled by law, some even think Monarchy or Communism is the path toward liberty… some, to the frustration of most everyone else, use liberty as an excuse to push their own special interests (as what is natural liberty if not deregulatory?).
We all agree liberty is one of the most important underlying concepts of humanity, but rarely do we agree on its meaning or the mechanics that it takes to achieve it.
According to John Locke’s Second Treatise of Government:
Or as Jefferson put it quoting Locke,
Of course this message isn’t much different than the one that Aristotle writes in his version of the Athenian Constitution (350 BC) where he quotes Solon (who lived in 600 BC). Or, that Aristotle himself writes in his masterwork Nicomachean Ethics.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.

Naturally occurring social systems are systems that naturally arise when societies form, such as politics, economics, mathematics, and language.
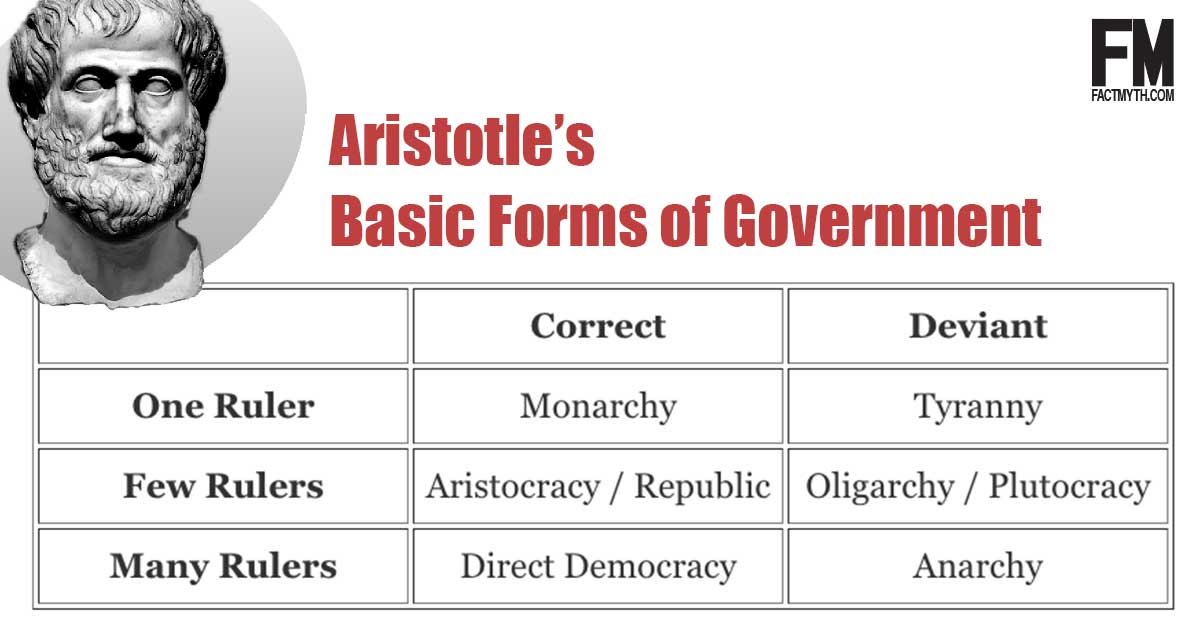
We explain and list the types of governments. We cover the basic classical forms of government, the many types of governments that can be derived from the classical forms, and the actual forms of governments in practice.

Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government.
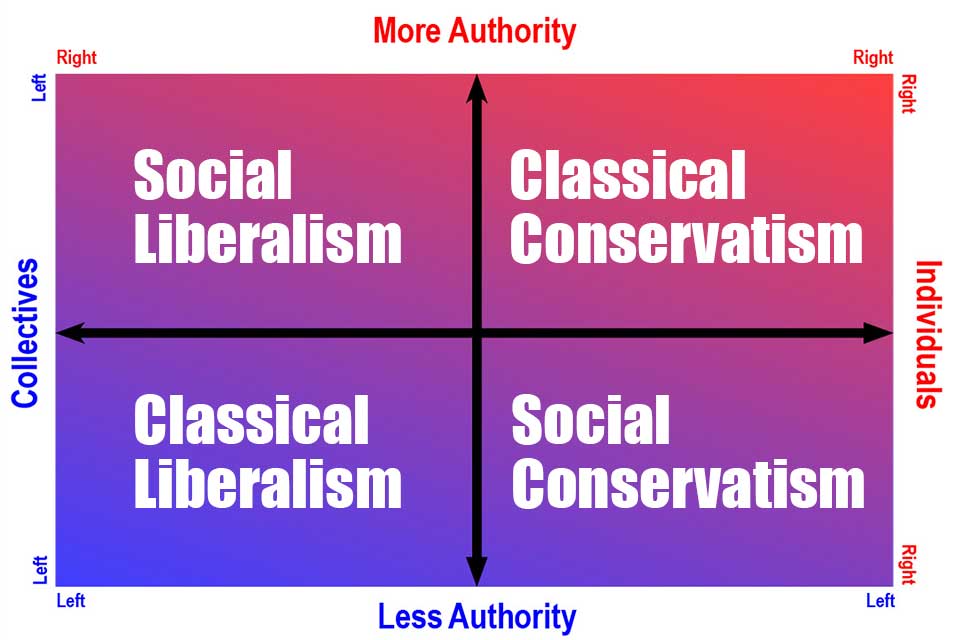
We explain liberalism and conservatism, including the different social and classical types of liberalism and conservatism.
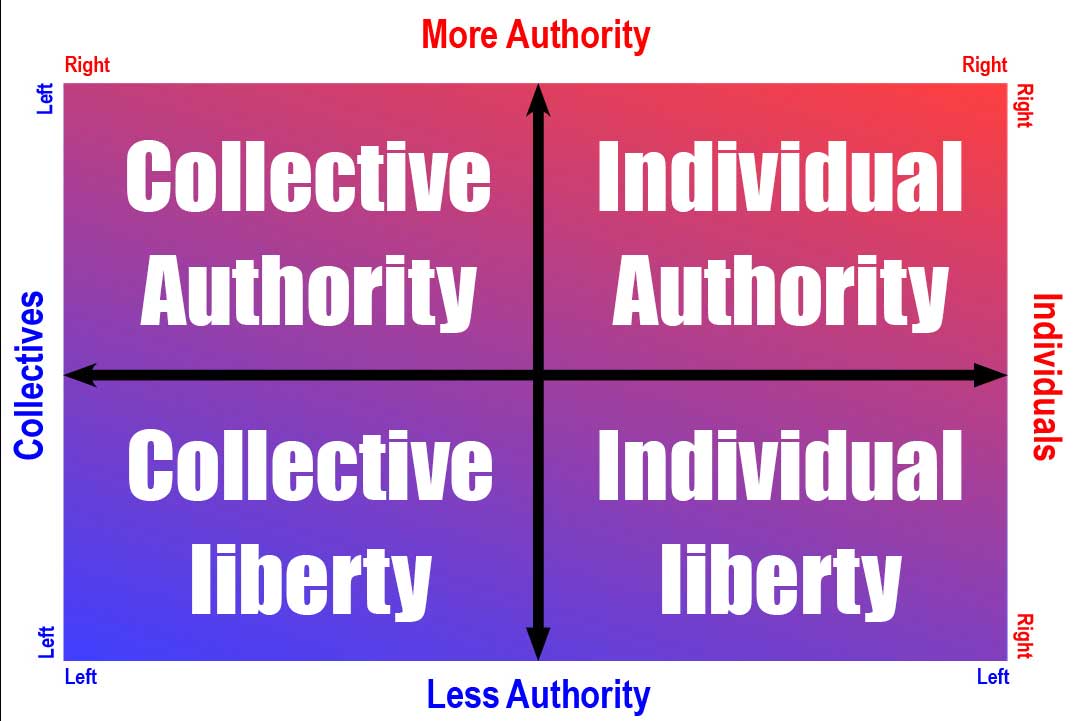
Collectivism describes ideology (political or otherwise) that favors the collective, like-wise Individualism describes ideology that favors the individual.

We explain Adam Smith as a Moral Philosopher, and explore how his Theory of Moral Sentiments connects to his economic theory from The Wealth of Nations.

We explain populism, globalization, nativism, nationalism, neoliberalism, modernization, and other terms important for understanding modern world politics.

The Federalists and Anti-Federalists were the first political factions of the U.S.. They arose out of a debate over the ratification of the 1787 Constitution and went on to form the basis of our current two-party system.

We present a summary of the history of human rights documents including the Bill of Rights, Magna Carta, Declaration of Rights and Man, and English Bill of Rights.