What is Liberalism?
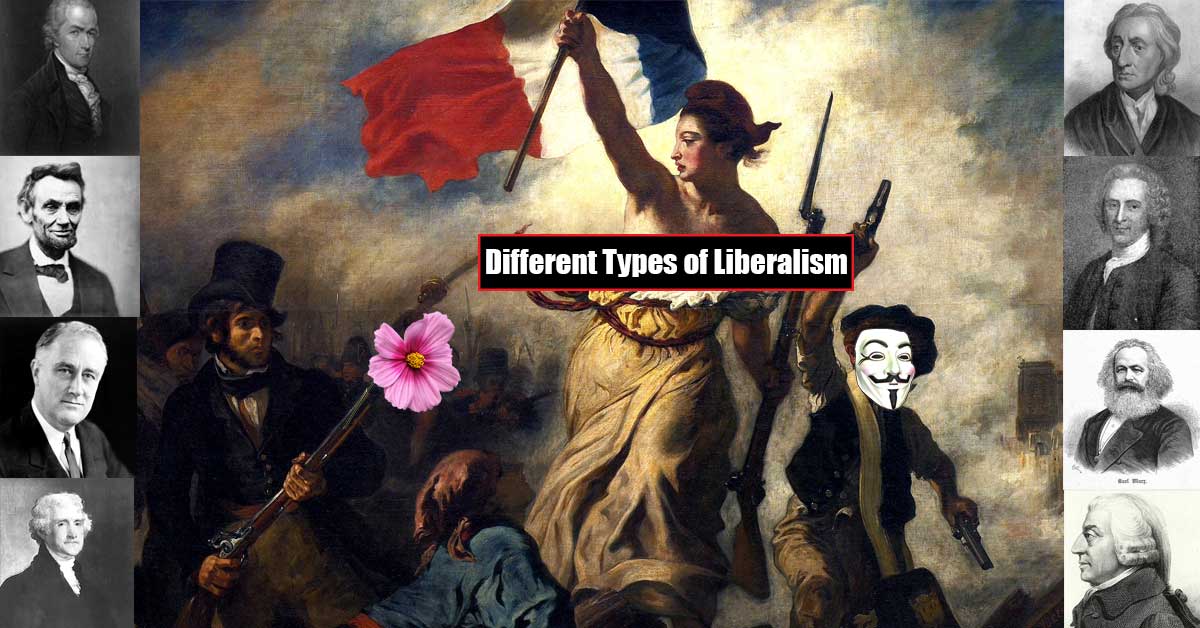
Liberalism is the political ideology of liberty and equality, where classical liberalism emphasizes individual liberty and social liberalism emphasizes social equality.

Liberalism is the political ideology of liberty and equality, where classical liberalism emphasizes individual liberty and social liberalism emphasizes social equality.
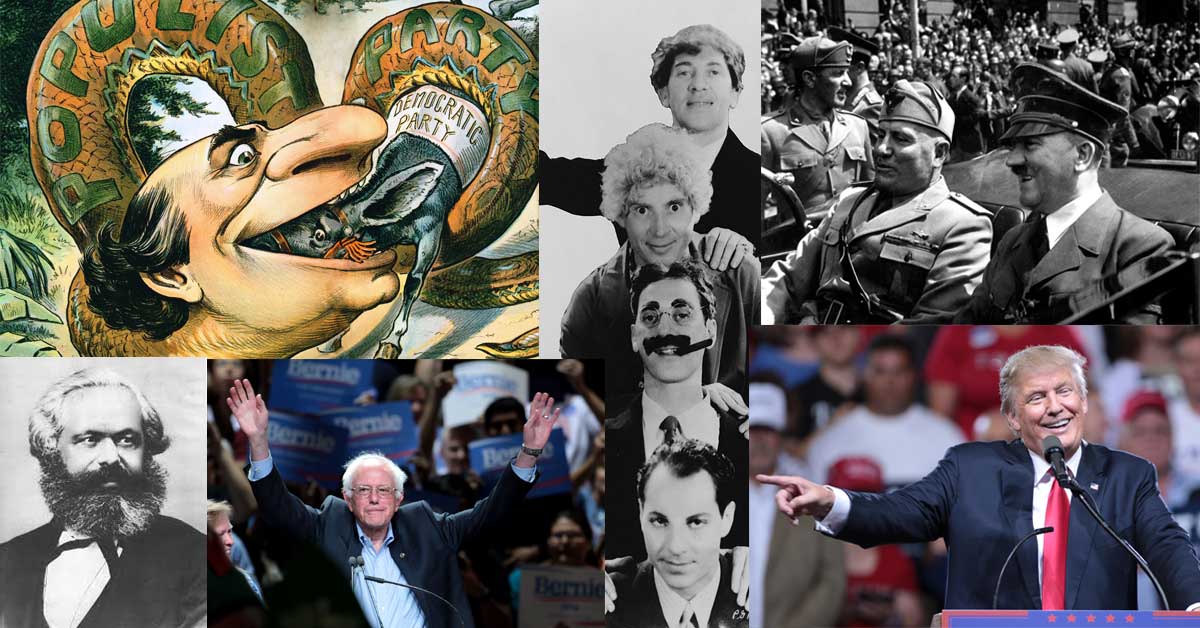

Populism is a broad term that generally describes popular sentiment felt by the working class against the elites. It can look like social conservative nativist right-wing populism or social liberal progressive left-wing populism.

We present a simple guide to Marx, Marxian class theory, Marx’s theory of history, and Marx’s economic theories to help westerners understand what Marx was all about.
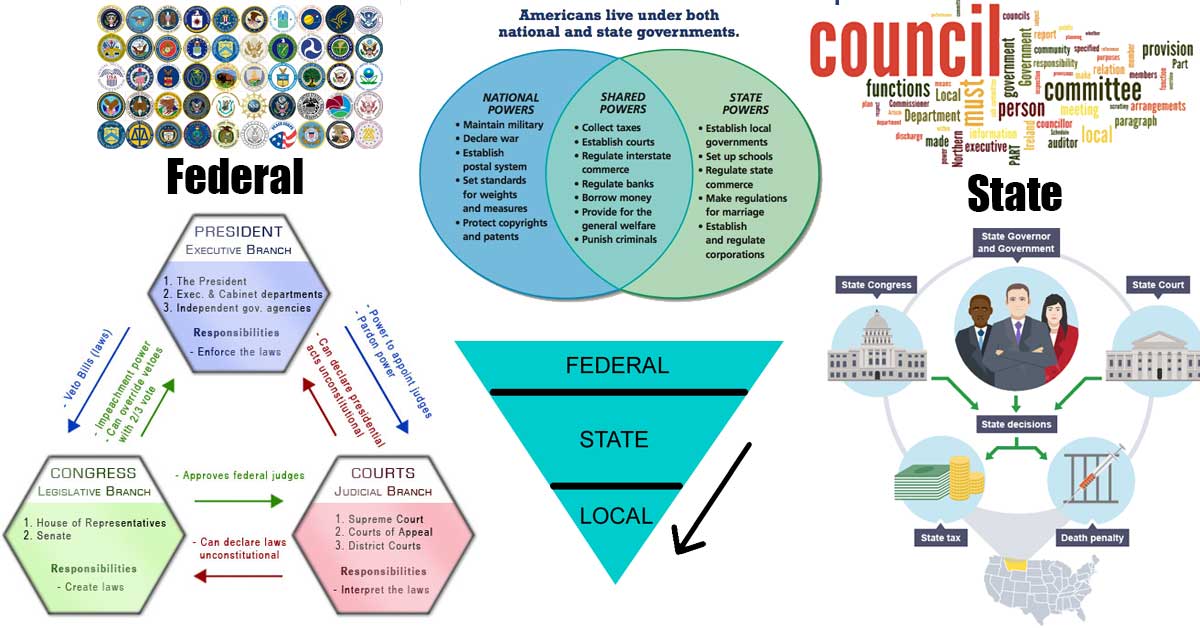
Separation of Powers describes the way in which government is divided into different branches (ex. in the U.S., the legislative, executive, and judicial). Checks and balances describe the powers each branch has to “check” the other branches and ensure a balance of power.
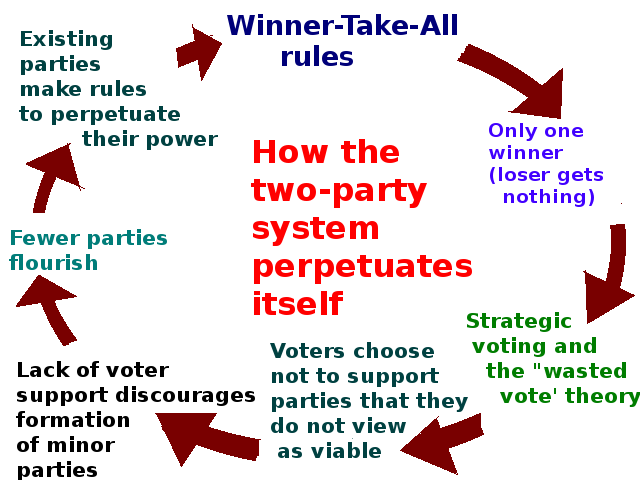
We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.

Different types of government can be said to be based on a number of attributes like power source, power structure, and economic system.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.
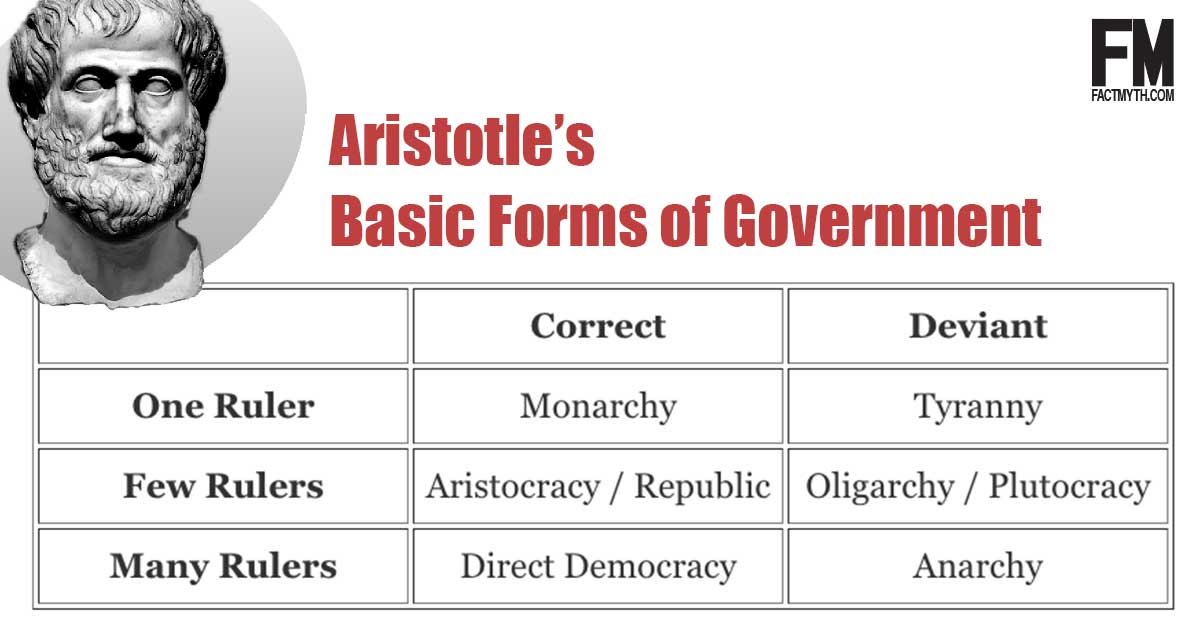
We explain and list the types of governments. We cover the basic classical forms of government, the many types of governments that can be derived from the classical forms, and the actual forms of governments in practice.

Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government.
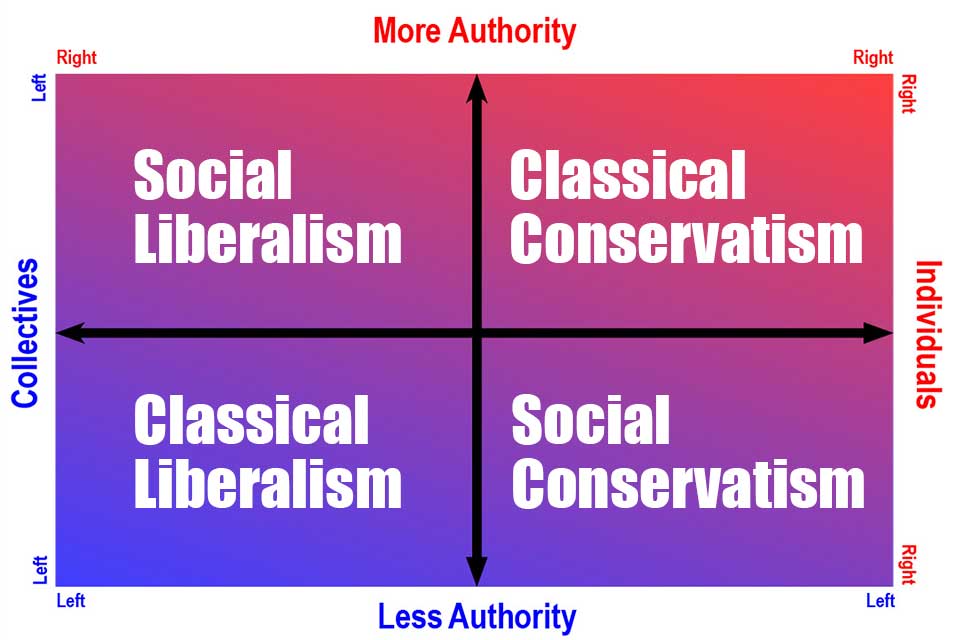
We explain liberalism and conservatism, including the different social and classical types of liberalism and conservatism.