The Black Vote and National Politics

We look at the effect of the black voter and black suffrage on the balance of political power in the two-party system.
Voting is the democratic process of government by consensus. At each election many races are held and many pieces of legislation are voted on.

We look at the effect of the black voter and black suffrage on the balance of political power in the two-party system.

The article below is written as advice to potential “faithless electors” thinking about how to vote in 2016, but doubles as a lesson in civics regarding the powers and responsibilities of the U.S. Electoral College.

We explain the different ways America can change the Electoral College system, and discuss the pros and cons of abolishing or reforming the electoral system.
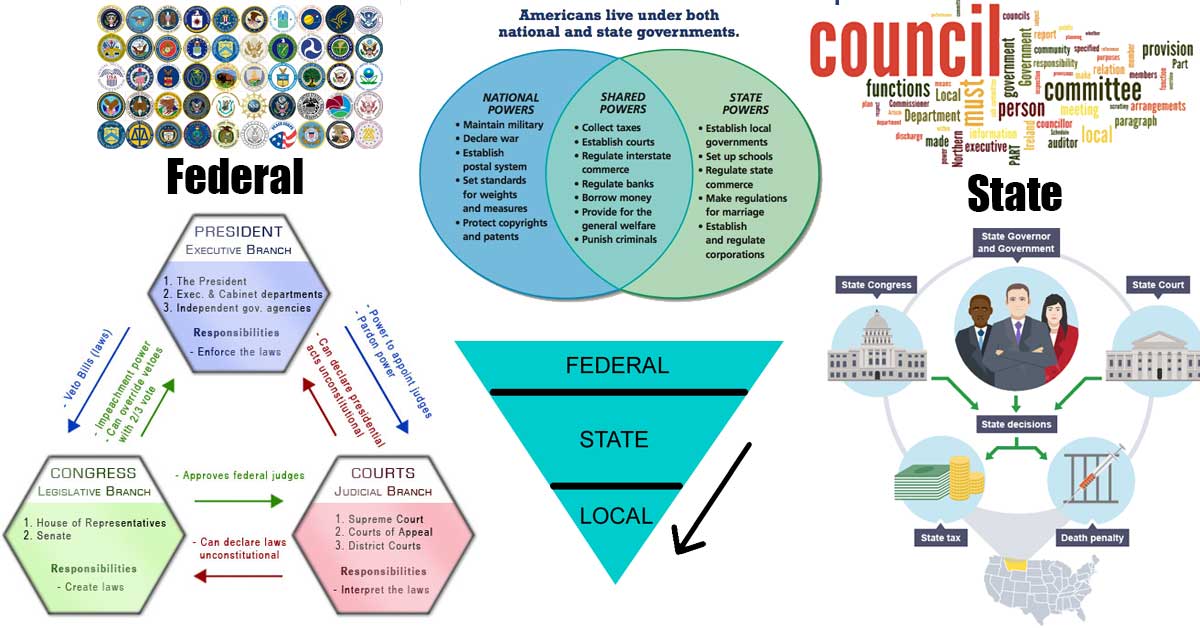
Separation of Powers describes the way in which government is divided into different branches (ex. in the U.S., the legislative, executive, and judicial). Checks and balances describe the powers each branch has to “check” the other branches and ensure a balance of power.

Different types of government can be said to be based on a number of attributes like power source, power structure, and economic system.