The Paradox Principle

In practice, human action often has paradoxical or unintended effects. Sometimes effects or side effects even have the exact opposite effect as intended.
The political terms left and right are comparative terms that describe political views as: liberalism, collectivism, and liberty (left) vs. conservatism, individualism, and authority (right).
Since political ideology is a complex spectrum of beliefs and actions, the terms are best applied with nuance. They can be used to make absolute statements like Monarchies are right-wing forms of government in terms of power structure. Or they can be used to make comparative statements such as, a progressive Democrat is to the right of a radical anarchist. See the pages below for detailed discussions into the aspects of the political left and right.

In practice, human action often has paradoxical or unintended effects. Sometimes effects or side effects even have the exact opposite effect as intended.

We examine the historical effects of social, political, and economic inequality on society to see how it has led to social unrest and events like revolutions and populist uprisings.
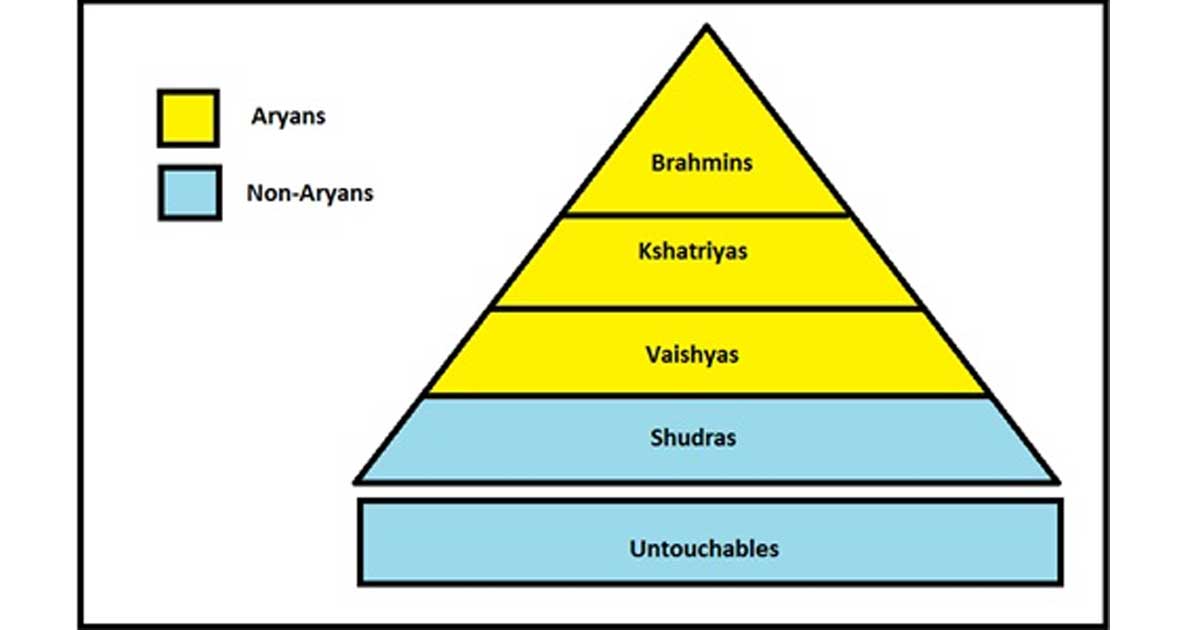
India’s caste system is a class system based on birth. These classes, or “Varnas”, are: Brahmins (priests), Kshatriyas (ruling and military), Vaishyas (merchants and farmers), Shudras (peasants), Dalits (untouchables).

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.

Villains tend to have mustaches, not because facial hair is evil, but because despots style themselves after other despots.

The exact origin of the term politically correct isn’t known, although the earliest usage we could find was from 1793 Supreme Court Case Chisholm v. Georgia.

Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government.

Plato can be understood as the father of rationalism and political philosophy (political idealism), and Aristotle, his student, the father of empiricism and political science (political realism).
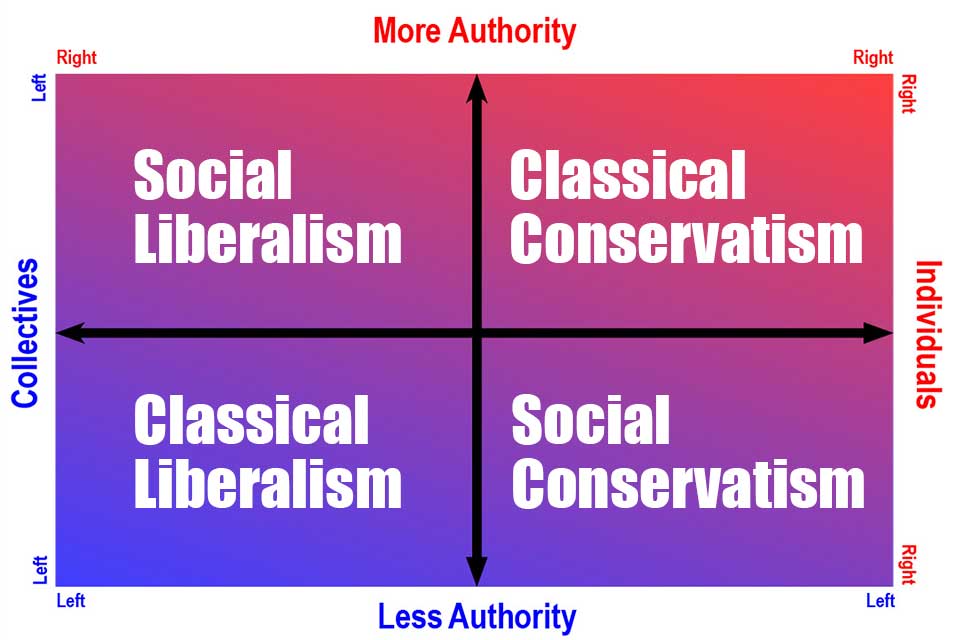
We explain liberalism and conservatism, including the different social and classical types of liberalism and conservatism.

Political realism is dealing with politics as they are in reality, political idealism is dealing with politics as an ideal.