What is Light?
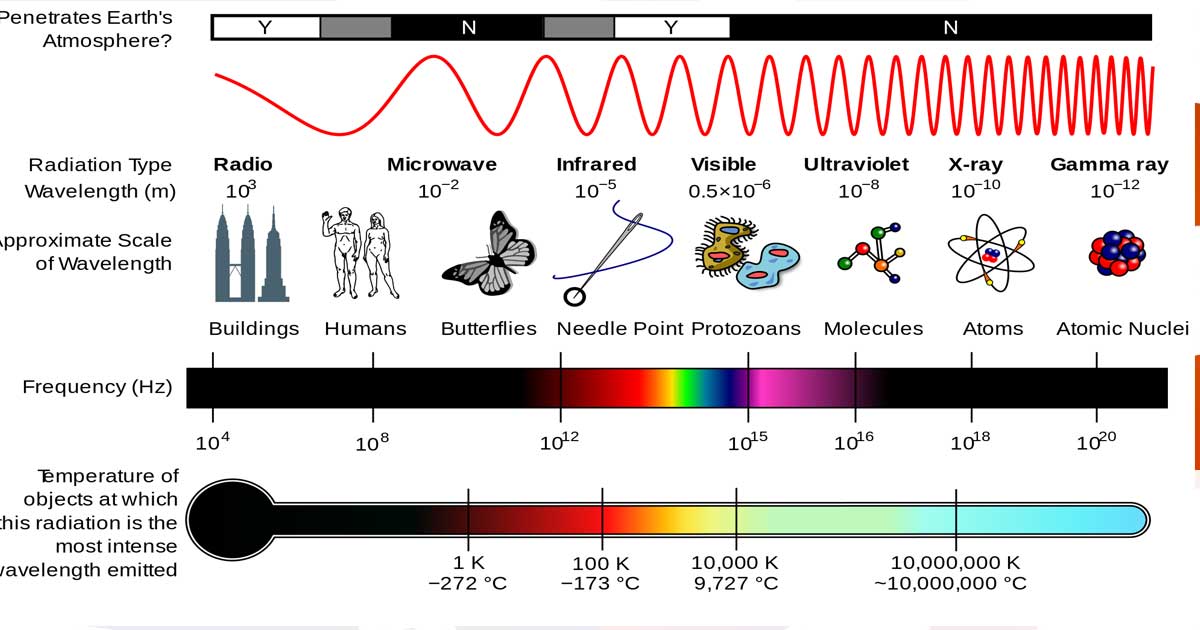
We explain “light,” both as electromagnetic radiation within a visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and as electromagnetic energy carried by photons.
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist whose theories of relativity, along side classic and quantum physics, creates the foundation of modern physics. Einstein is best known for his mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2 (energy equals mass multiplied by the speed of light squared). E = mc2 shows that mass and energy have equivalent mathematic value using the speed of light as a conversion factor, and can be thought of as mass-energy (a count of the total potential and kinetic energy of a system of one or more particles).
Understanding Einstein isn’t always easy, but it is rewarding. Check out this Yale University Lecture on Einstein for the Masses, or this video on How Einstein Used Intellectual Play to Create Our View of Reality, or check out the Einstein facts and myths below.

We explain “light,” both as electromagnetic radiation within a visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and as electromagnetic energy carried by photons.

We present a discussion on “the meaning of life as happiness,”the Greatest Happiness Theory,” “the Good Life,”the Pursuit of Happiness,” and Virtue Theory.
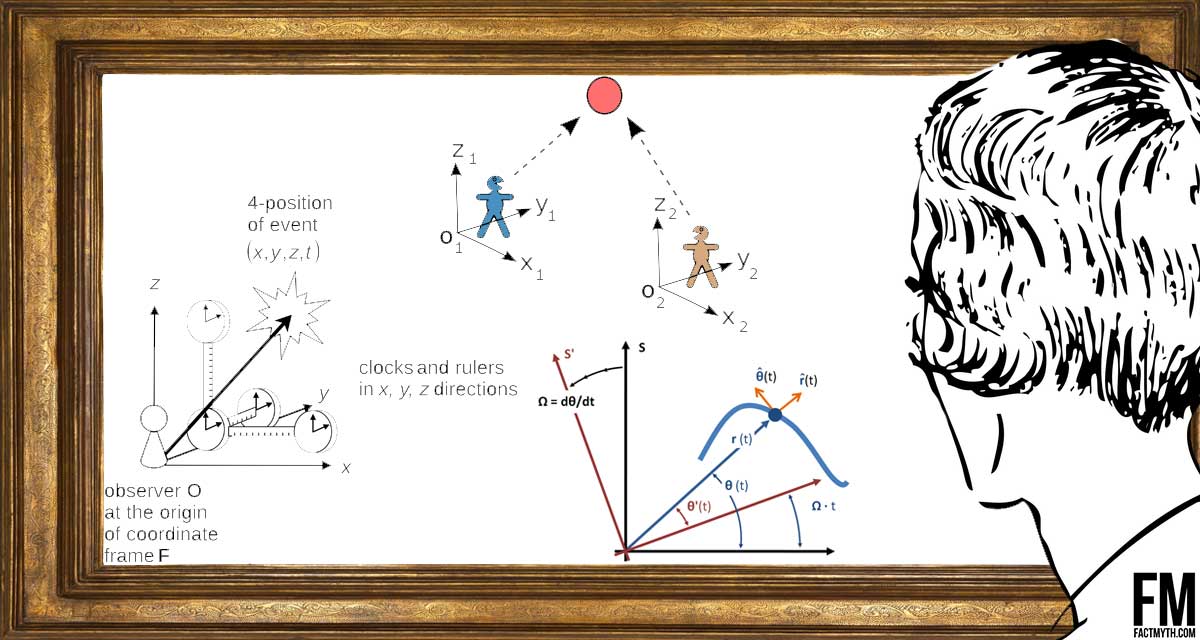
Reference frames and relativity in physics explained using math-free examples. We cover: frames of reference, inertial frames, accelerated frames, and relativity.