The Dunning–Kruger Effect

The Dunning–Kruger effect is when people over-estimate their competence in something due to a lack of experience in that thing.
Bias is a prejudice for or against. In broad terms we can think of our entire neurology as a system of hardwired and softwired bias. Given this, it is vital to understand that bias isn’t “a bad thing” and is rather an integral part of our cognitive process.

The Dunning–Kruger effect is when people over-estimate their competence in something due to a lack of experience in that thing.

As an independent fact-checking site we fact-check a range of touchy subjects… and sometimes people get upset with us for not validating their conspiracy theories.
I would argue that most sources of information and any information they contain should not be dismissed due our thoughts on them in general or a portion of their content. Instead, I would argue that any source is capable of presenting good and useful information, even if they typically don’t.
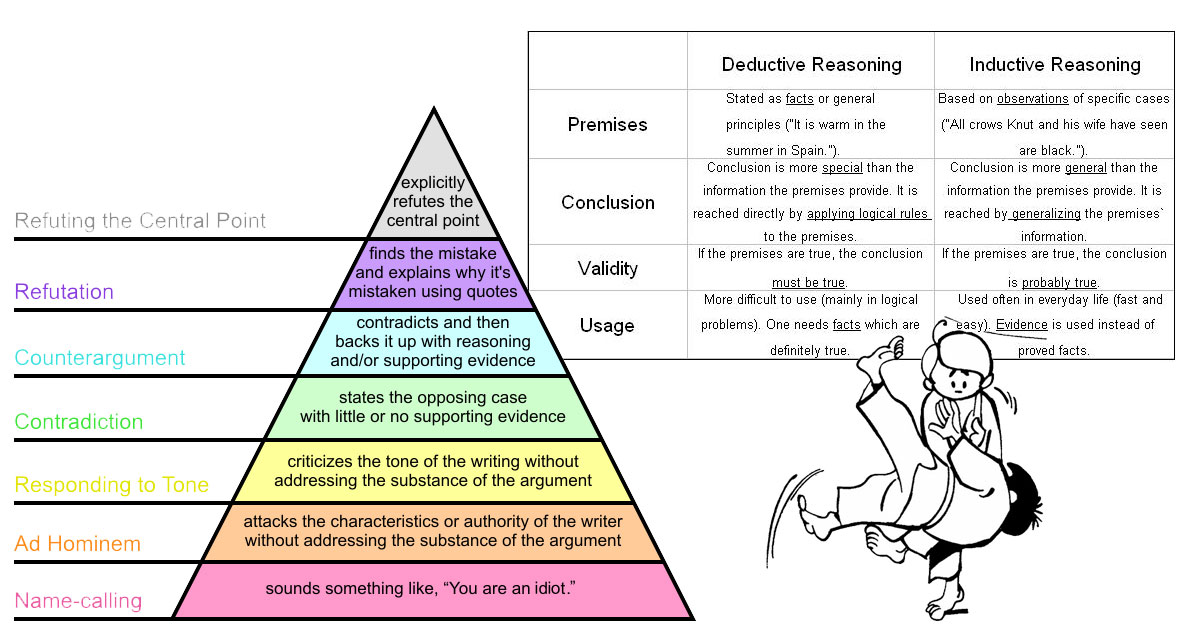
We present a list of types of propaganda, propaganda techniques, and propaganda strategies used to manipulate public opinion in the modern day.
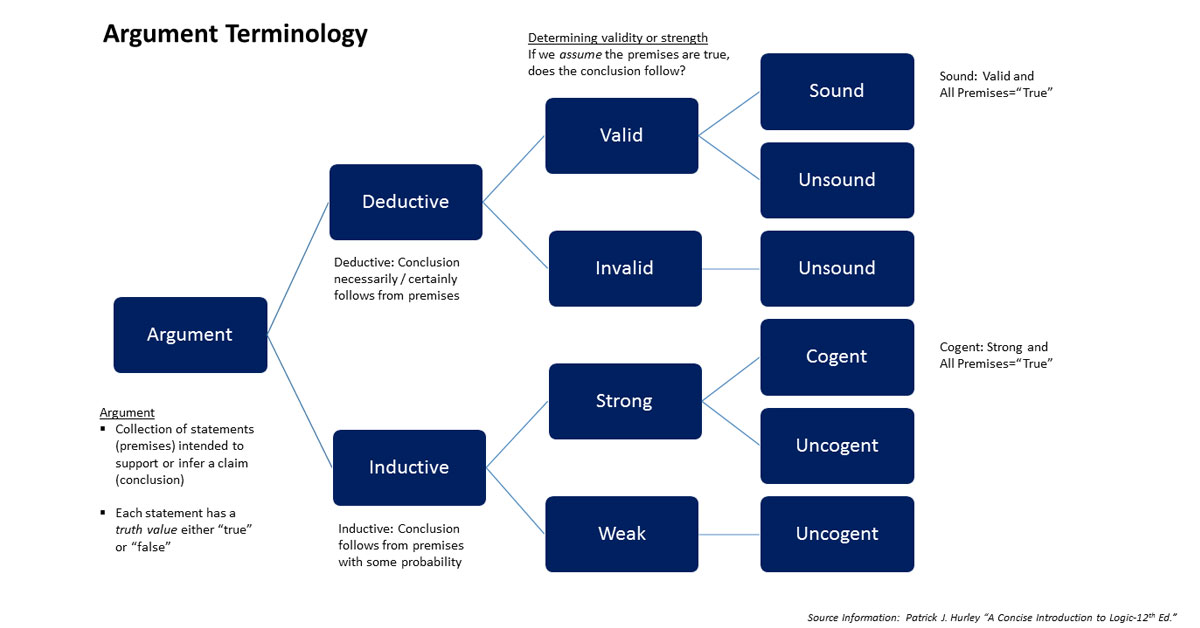
We explain and compare the different types of reasoning methods including deductive, inductive, abductive, analogical, and fallacious reasoning.

We explain how experience and social interactions shape our frame of reference and create ideological bubbles, and how this creates confirmation bias and “bubble filters” that reinforce these bubbles.

We discuss racial code words and “dog-whistle politics,” terms that describe the code words politicians use to imply politically incorrect ideas to their base.

Explicit bias is conscious bias, implicit bias is subconscious bias. Everyone has natural implicit and explicit bias, it’s part of being human and what shapes our actions and attitudes.

The bed of nails principle states that while laying on one nail is enough to puncture a person’s skin, laying on many distributed nails isn’t.

We explain paradoxes related to tolerance and Politically Correctness (PC), including “the paradox of tolerance” and “tolerance as a form of intolerance.”