Vices and Virtues Explained

We present a list of vices and virtues and look at vices and virtues as understood by philosophers like Aristotle and Aquinas.
Plato (428-347 BC), his teacher Socrates, Plato’s teacher Aristotle (384-322 BC), their Sophist opposition, and other key Greeks helped lay the foundation of most western knowledge.
Plato was an idealist, Aristotle a Realist, but both were polymaths and lecturers whose books lay the foundation of physics, philosophy, social science, and more.
Meanwhile they both argued more for philosophy (a love of wisdom) over sophistry (teaching for money and thinking one “already knows”).

We present a list of vices and virtues and look at vices and virtues as understood by philosophers like Aristotle and Aquinas.
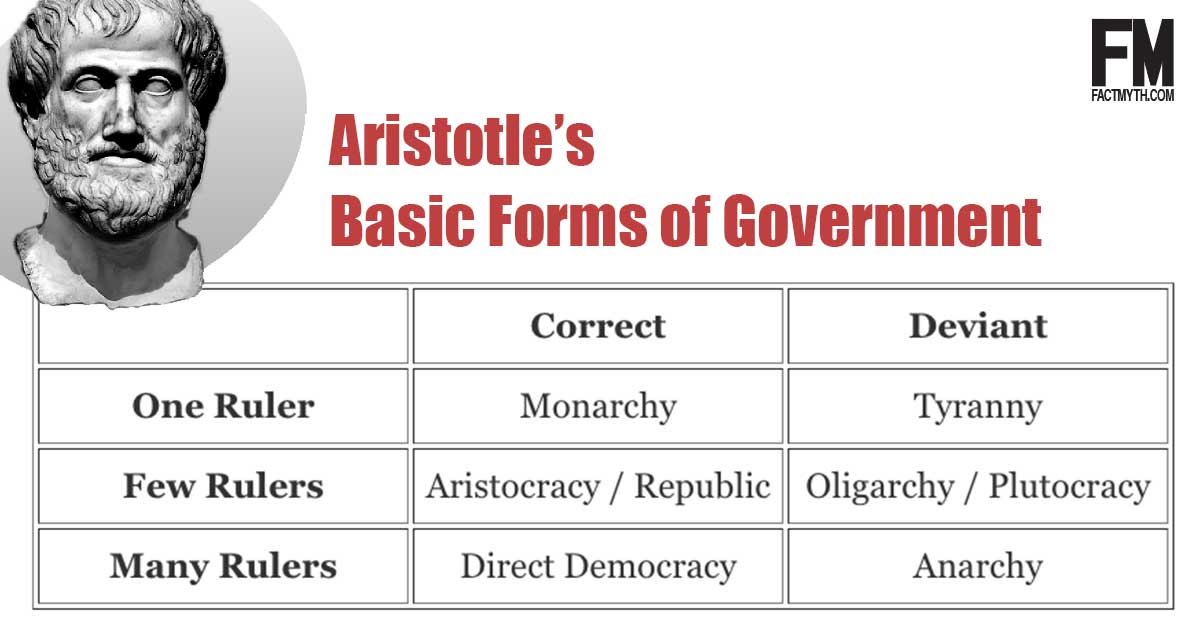
We explain and list the types of governments. We cover the basic classical forms of government, the many types of governments that can be derived from the classical forms, and the actual forms of governments in practice.

Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government.

Essentialism is the idea that everything has an essence (something that “makes it, it”). Existentialism says there is no essence (no intrinsic meaning that can be confirmed by the senses or reason).

Plato can be understood as the father of rationalism and political philosophy (political idealism), and Aristotle, his student, the father of empiricism and political science (political realism).

Political realism is dealing with politics as they are in reality, political idealism is dealing with politics as an ideal.

We explain economic inequality from a historical perspective, and then consider the effects of wealth inequality and income inequality in America today.

The major branches of philosophy can be denoted as: metaphysics (what is), epistemology (what we can know), logic and reason, ethics and morality, and aesthetics (beauty and art).

We present a discussion on “the meaning of life as happiness,”the Greatest Happiness Theory,” “the Good Life,”the Pursuit of Happiness,” and Virtue Theory.

Areté roughly means “moral virtue”. It refers to an innate “excellence” or “essence” in all things, and the striving toward that potential or purpose.