What is Light?
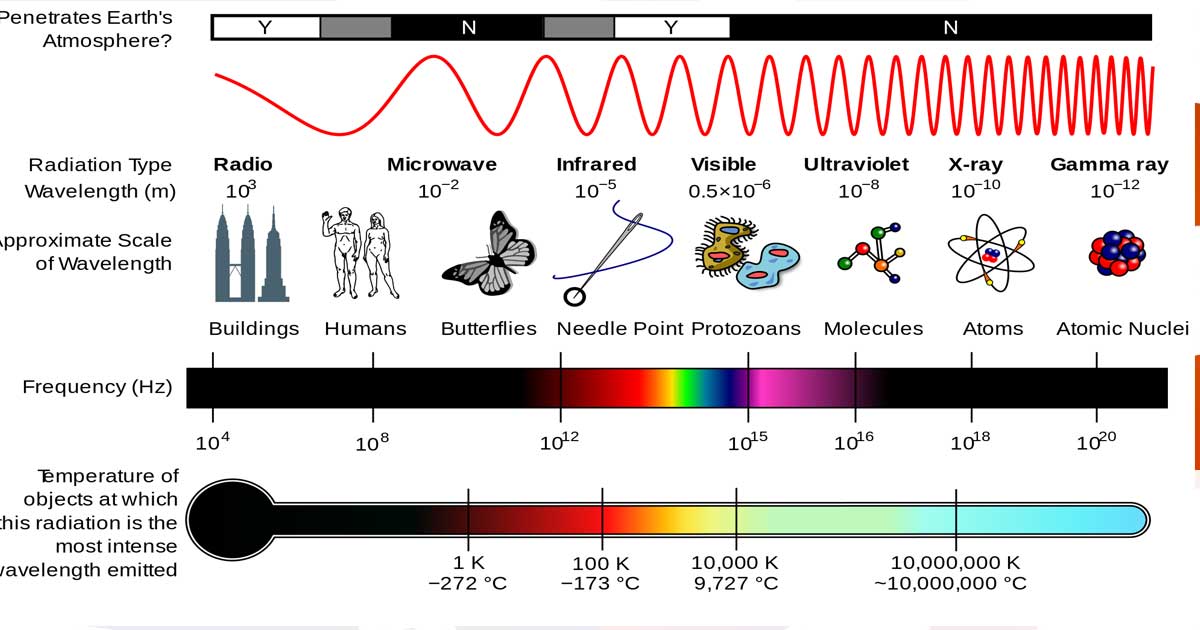
We explain “light,” both as electromagnetic radiation within a visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and as electromagnetic energy carried by photons.
Quantum Mechanics (AKA quantum physics or quantum theory) is a branch of physics concerning atomic and sub-atomic particles. Quantum mechanics gets it’s name from the fact that at a very small level things quantize to multiples of the Planck constant. The general concept behind quantum mechanics is represented by the standard model of particle physics (easier than it sounds) and rests upon classical physics and related equations (Maxwell, Einstein, Planck, Heinsberg, and many more). The concepts are heady, but the gist isn’t, it just takes a little spacetime and mass-energy.
See our standard model of particle physics simple explainer for a simple overview.

We explain “light,” both as electromagnetic radiation within a visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and as electromagnetic energy carried by photons.
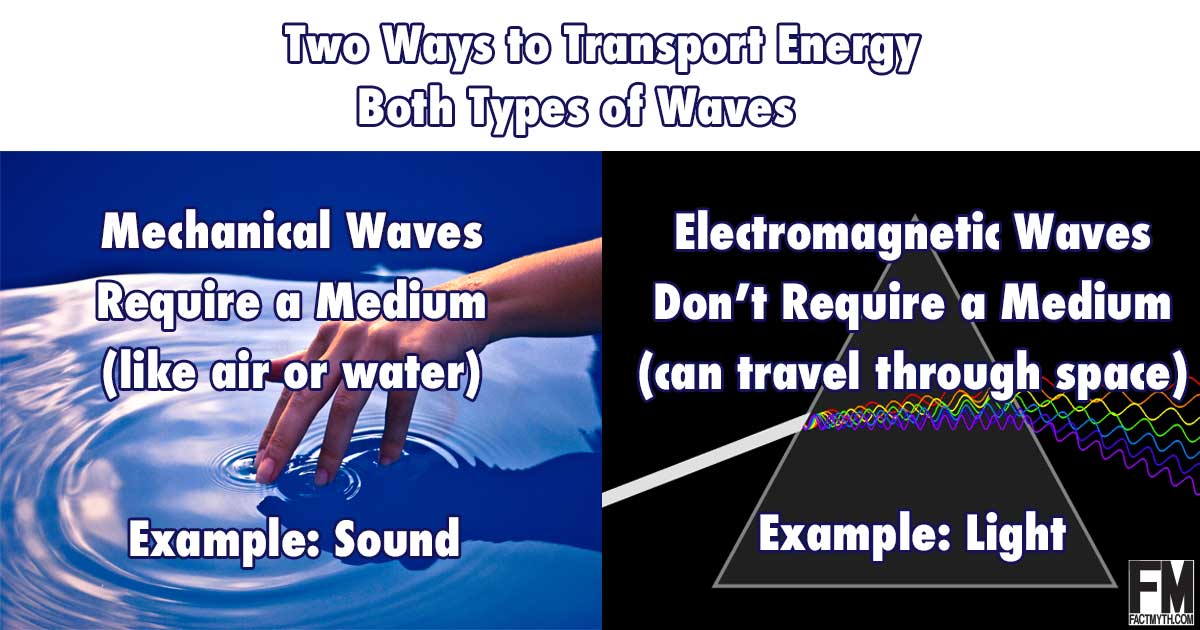
There are two types of waves: mechanical waves like sound that must travel through a medium like air, and electromagnetic waves like light that don’t.

The physical constants are measurable properties of the physical universe that don’t change, everything else is relative to these constants.
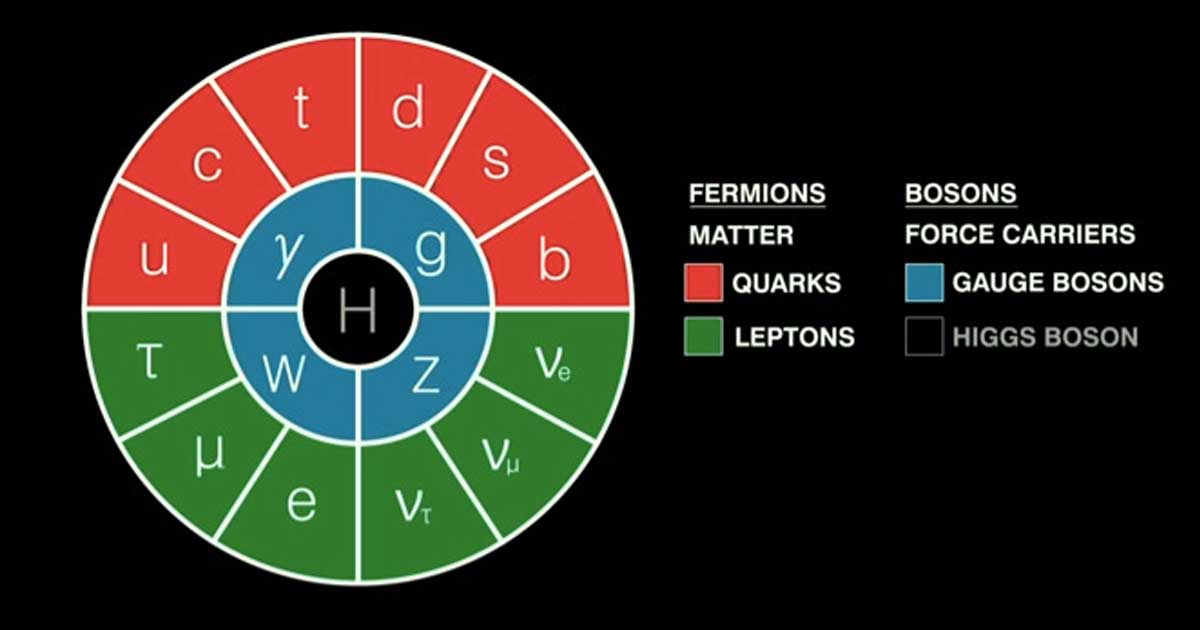
We explain the standard model of particle physics in simple terms for non-experts using videos, facts, and bullet points.