Types of Conflict Theories

We explain Marx’s conflict theory and other conflict theories to show how tension between social, political, material, and other forces manifest.
Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government. If we accept the logic of social contract theory, which we should as it is essentially a concept at the heart of all legal political theory, we can then look to its implications regarding the structure of the state and the spirit of the laws.

We explain Marx’s conflict theory and other conflict theories to show how tension between social, political, material, and other forces manifest.
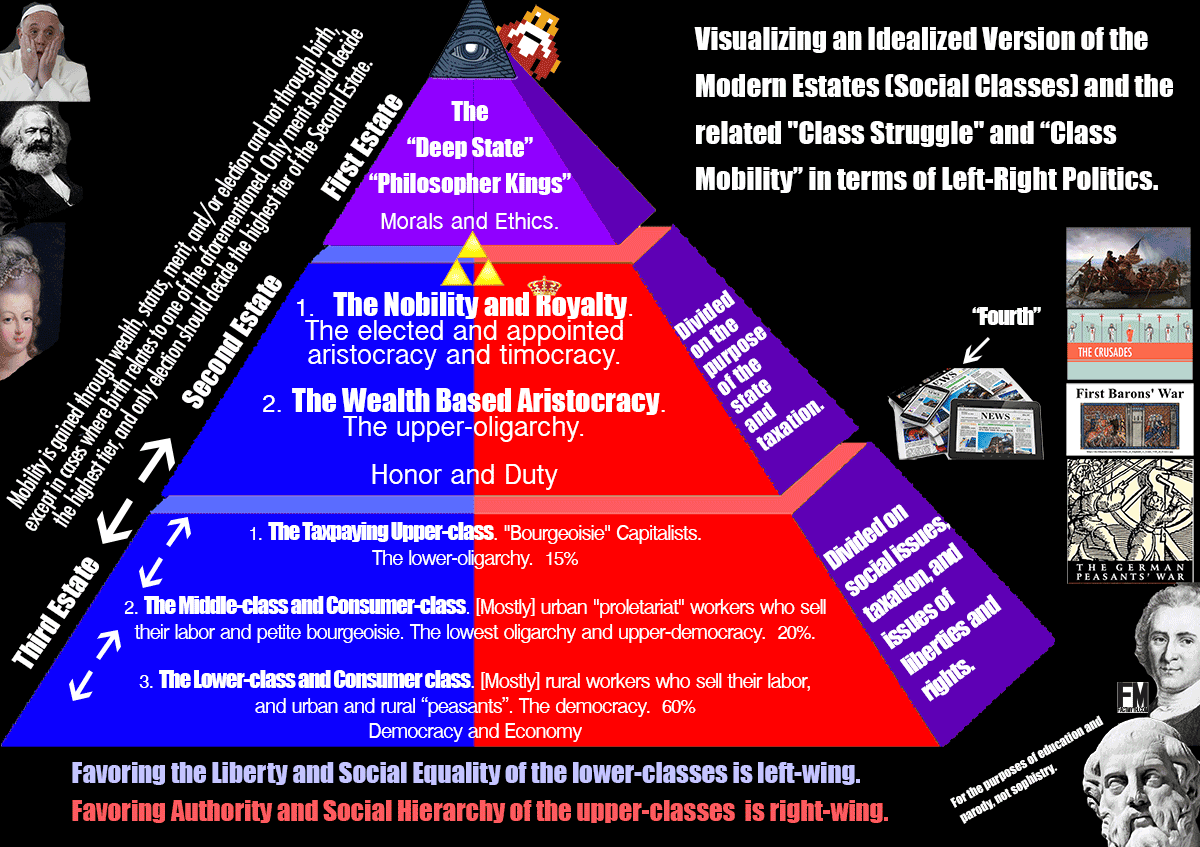
All nations have some sort of class system or class structure, generally based on wealth, birth, or status. We explain modern and historic social class systems and the general logic behind them to see to what extent they are natural and what extent they are convention.

“Civil Religion” is the civic “religion” of a nation. It doesn’t describe the theological religion of a nation, but rather a quasi-religious shared identity built around national symbolism and customs.

We often attribute the origin of the state of nature argument to Hobbes, but it can be traced to thinkers like Plato, Aristotle, and the Sophists in the 300s BC, and is then mused on by other early philosophers.

The state of nature is the state humans lived in before forming the first societies. By examining the state of nature we can better understand the implicit and explicit social contracts which govern societies.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s concept of the General Will roughly means “that which is in the best interest of the people” or “the public good”, and not just popular consensus.

Naturally occurring social systems are systems that naturally arise when societies form, such as politics, economics, mathematics, and language.
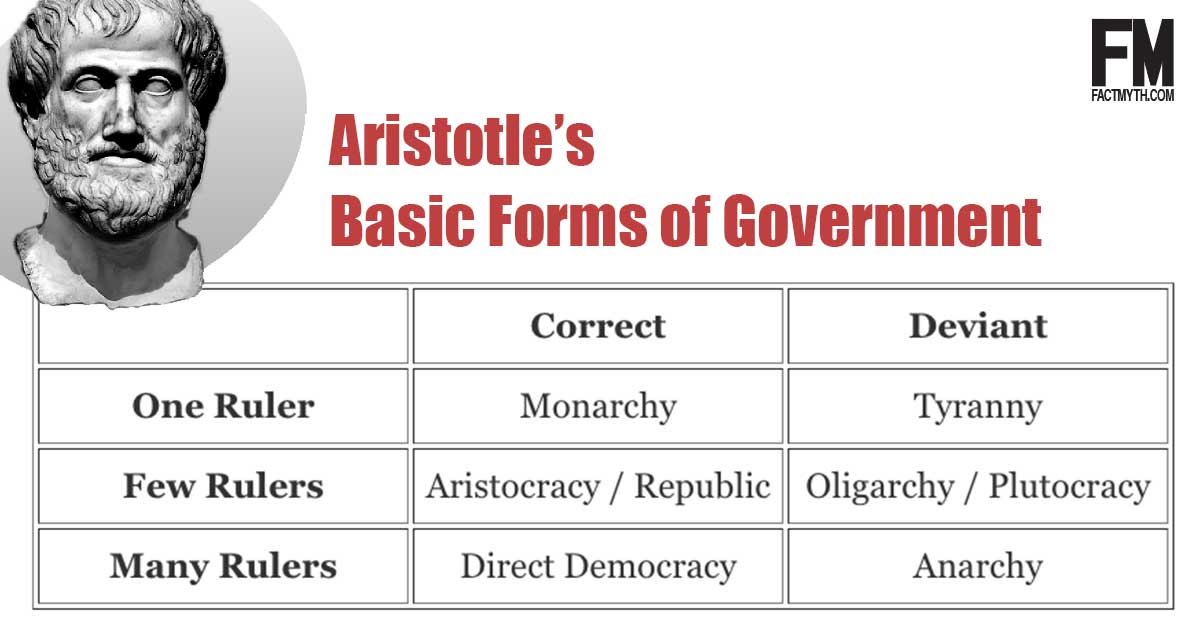
We explain and list the types of governments. We cover the basic classical forms of government, the many types of governments that can be derived from the classical forms, and the actual forms of governments in practice.

Social Contract Theory is the theory of why people form governments based on how people lived in a State of Nature before government.