Understanding Marx and Marxian Class Theory

We present a simple guide to Marx, Marxian class theory, Marx’s theory of history, and Marx’s economic theories to help westerners understand what Marx was all about.

We present a simple guide to Marx, Marxian class theory, Marx’s theory of history, and Marx’s economic theories to help westerners understand what Marx was all about.

Civil War, Revolution, and Rebellion all refer to different types of disputes between citizens of country regarding governmental power or authority.

“Civil Religion” is the civic “religion” of a nation. It doesn’t describe the theological religion of a nation, but rather a quasi-religious shared identity built around national symbolism and customs.
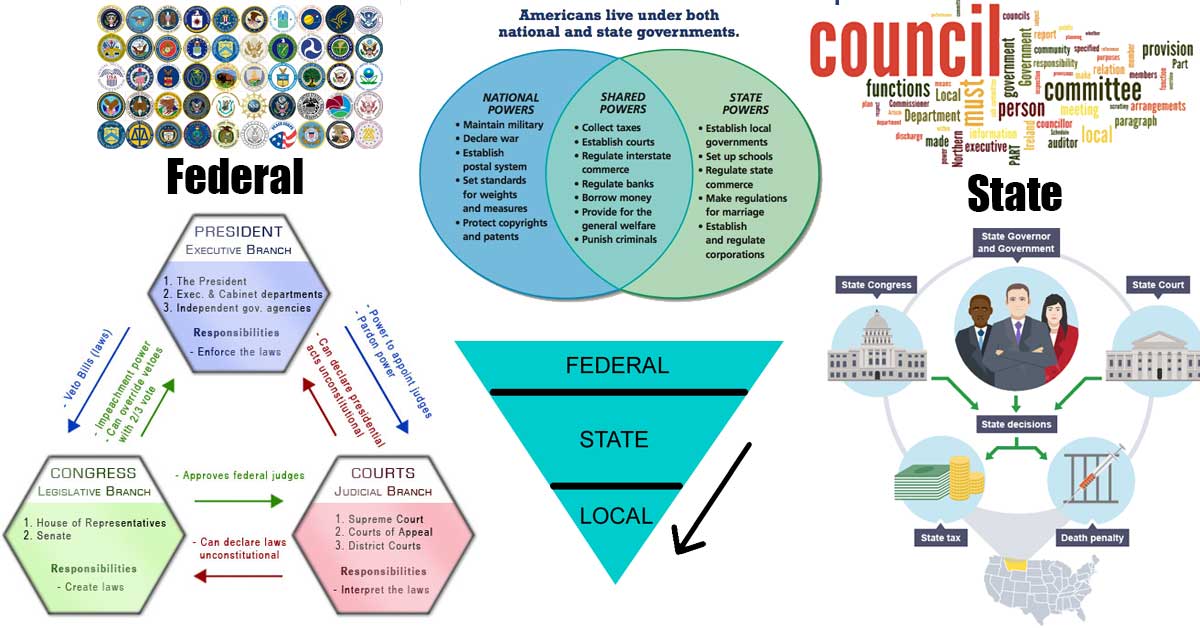
Separation of Powers describes the way in which government is divided into different branches (ex. in the U.S., the legislative, executive, and judicial). Checks and balances describe the powers each branch has to “check” the other branches and ensure a balance of power.
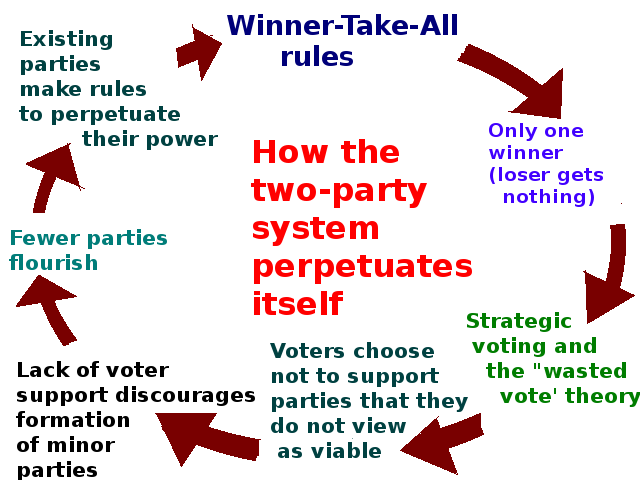
We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.
In modern history political factions have often been represented by a color, we look at political color to understand color politics.

In America we have a Progressive Federal Income Tax system broken down into “tax brackets”. Tax Filers pay the “marginal tax rate” on each dollar of income in a given bracket (after most deductions, but before tax credits).

We explain neoliberalism, globalization, nativism, and protectionism and the pros and cons of “neoliberal globalization” and “nativist protectionism.”
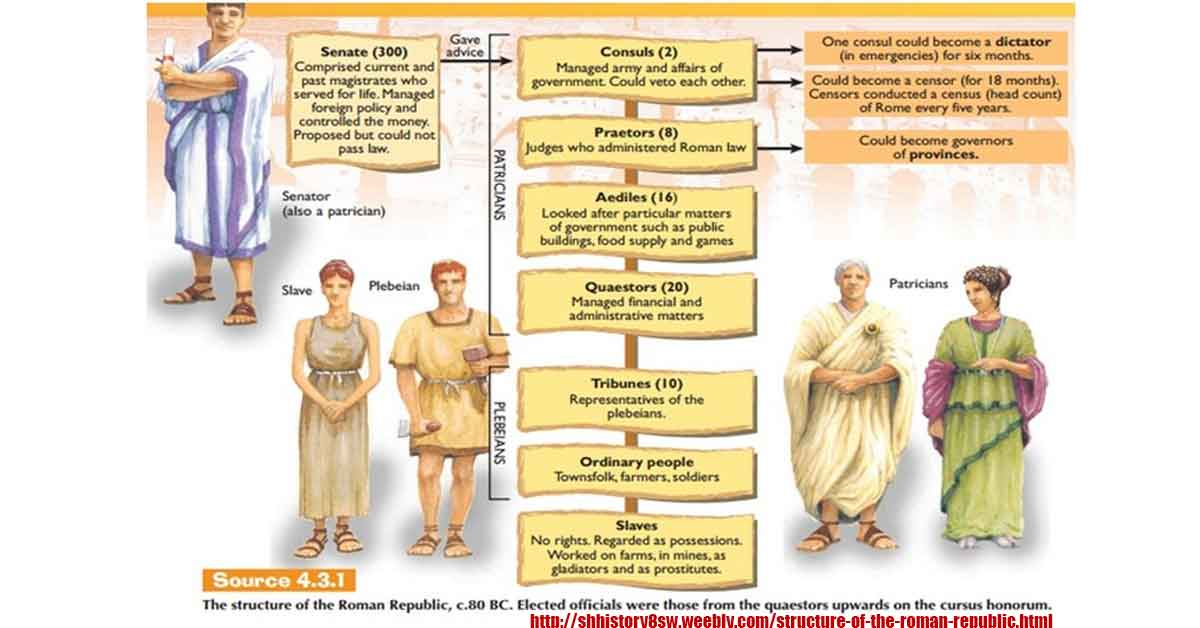
The Optimates like Pompey (aristocrats) and Populares like Julius Caesar (populists) were two opposing political factions at the onset of the fall of the Roman Republic.
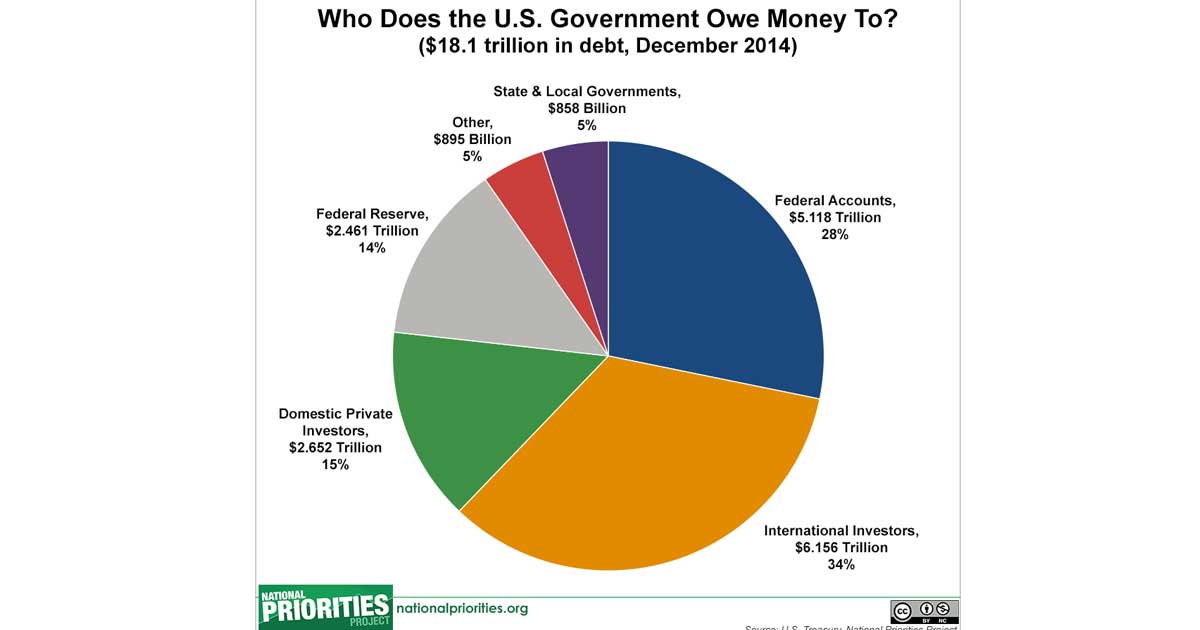
Below we explain how currency gets into circulation via the Treasury, Federal Reserve, and banks, and the role Congress, banks, businesses, and you play in the process.