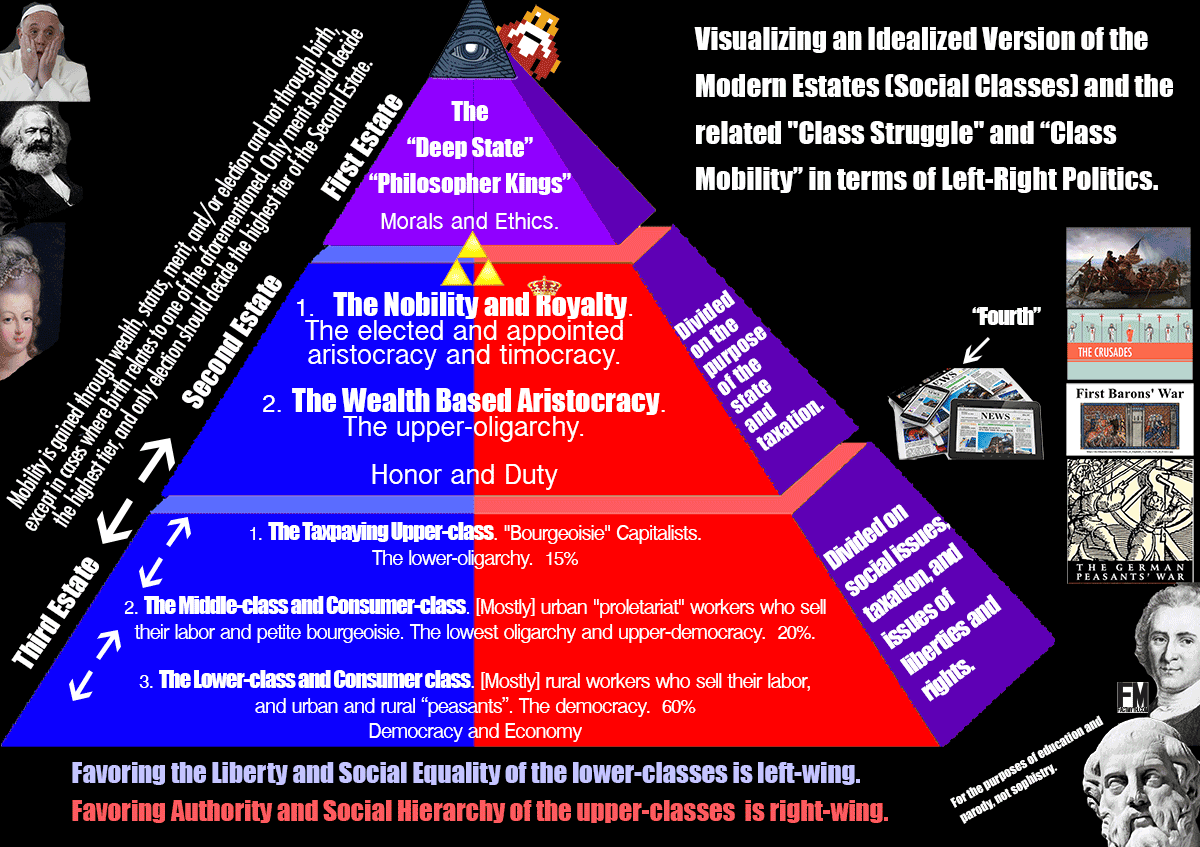
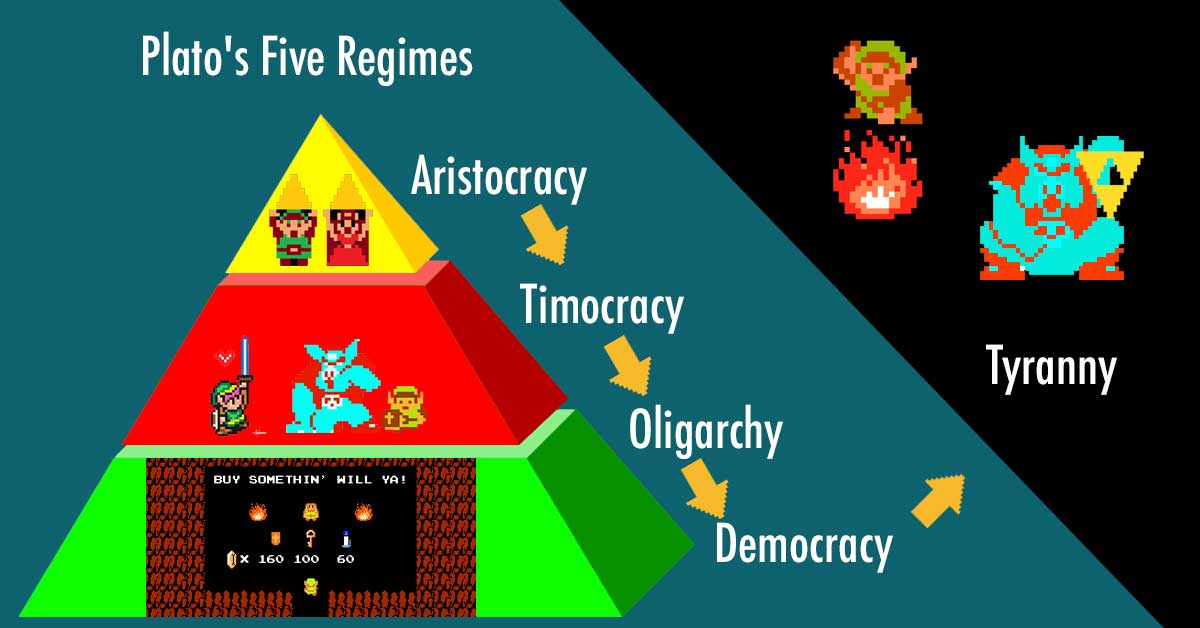
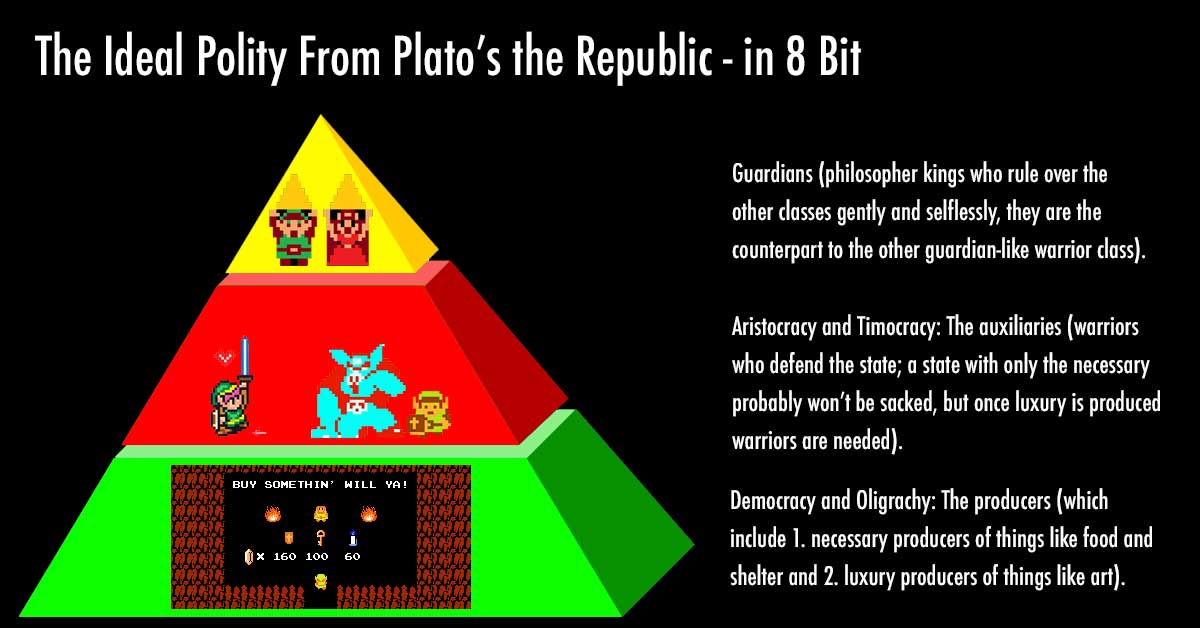
The Seisachtheia [The Relief of Burdens]; a Cancellation of All Debts
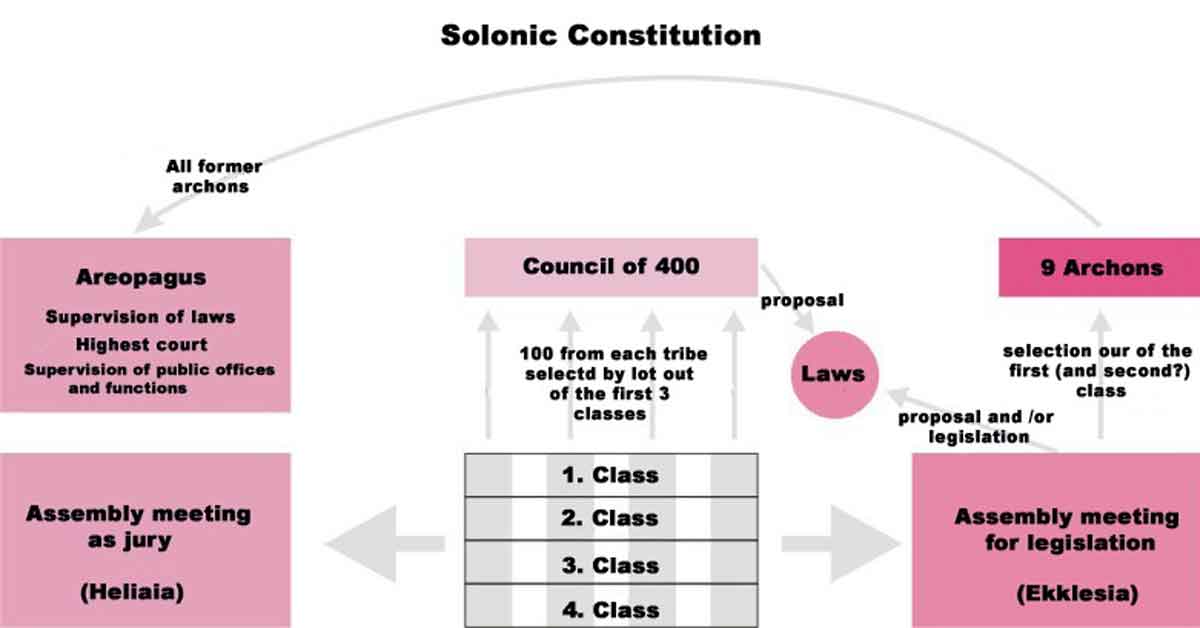
The Athenian Constitution tells the story of how Solon liberated the people by cancelling all debts, public and private. This was called the Seisachtheia [the removal of burdens or relief of burdens]. It is an example of what we might today call “a great reset.”