Saul Alinsky is the Father of Modern Community Organizing

Saul Alinsky, the American community organizer and author of Rules for Radicals, can be considered the father of modern community organizing.
Society refers to groups of people the cultures they form.

Saul Alinsky, the American community organizer and author of Rules for Radicals, can be considered the father of modern community organizing.

We explore the nature of truth, the different types of truth, and the different types of entities who report truth to better understand the nature of information.

We explain two types of special interests: cronyism (politicians working with corporate interests) and monopolies / oligopolies (the consolidating of corporate power in a given industry to one or few entities).
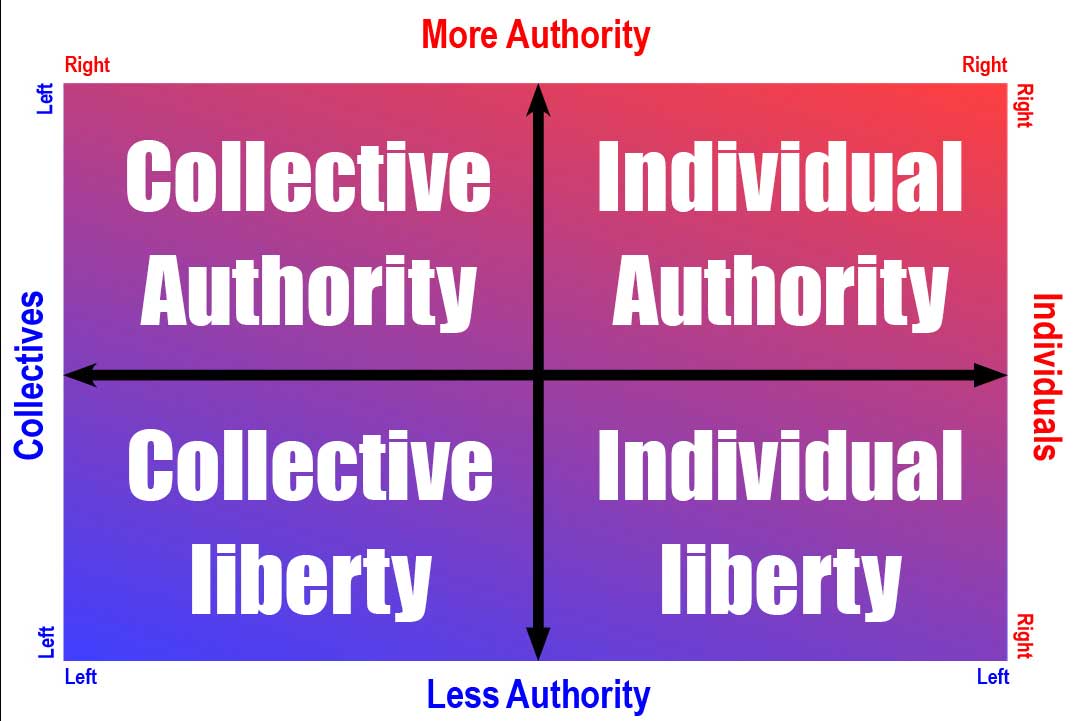
Collectivism describes ideology (political or otherwise) that favors the collective, like-wise Individualism describes ideology that favors the individual.

Some claim the Second Amendment, like the Three-Fifths Compromise, was ratified to preserve slavery. This is only partially true.
Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, and other Barons of Industry freely gave away most of their fortunes to charitable and philanthropic causes.

We explain populism, globalization, nativism, nationalism, neoliberalism, modernization, and other terms important for understanding modern world politics.

The Declaration of Independence was voted on July 2nd, 1776 and signed July 4th, 1776, but independence wasn’t officially gained until the signing of the Treaty of Paris on September 3, 1783.

The Federalists and Anti-Federalists were the first political factions of the U.S.. They arose out of a debate over the ratification of the 1787 Constitution and went on to form the basis of our current two-party system.

Alexander Hamilton founded the Federalist Party, the world’s first voter-based political party, which helped shape America’s economic policy and power structure.