Saul Alinsky is the Father of Modern Community Organizing

Saul Alinsky, the American community organizer and author of Rules for Radicals, can be considered the father of modern community organizing.
Politics is the science, art, and theory of influence and governance.
“Governing a country is like cooking a small fish, if handled correctly the results will be good”. – Lao Tzu

Saul Alinsky, the American community organizer and author of Rules for Radicals, can be considered the father of modern community organizing.

We explain two types of special interests: cronyism (politicians working with corporate interests) and monopolies / oligopolies (the consolidating of corporate power in a given industry to one or few entities).
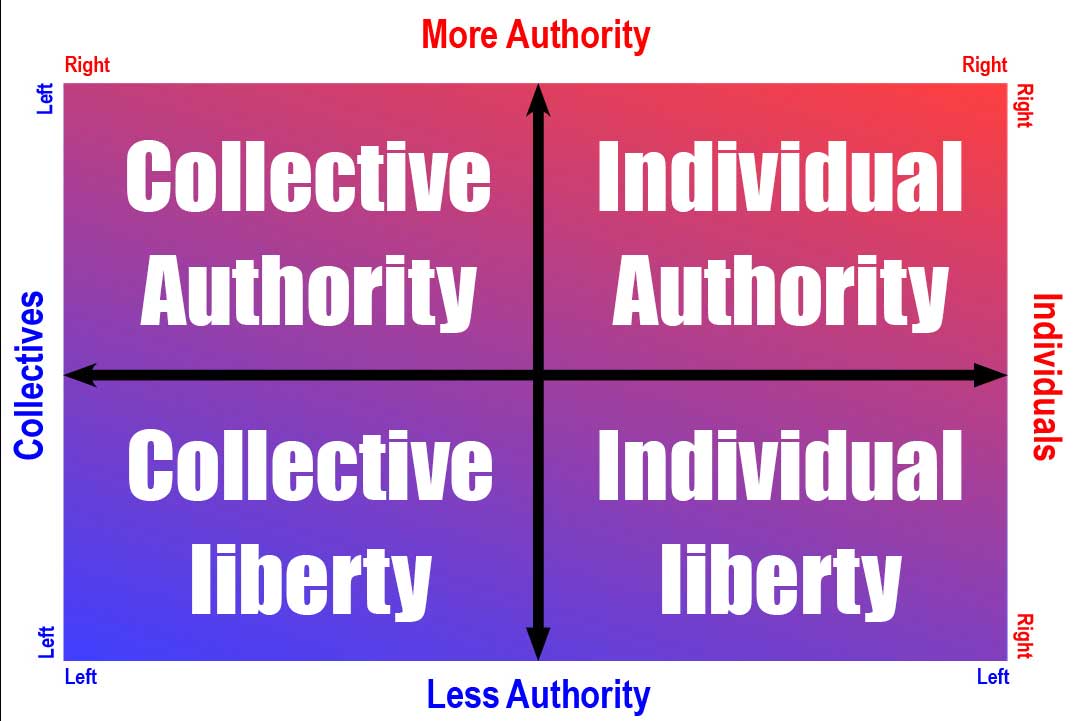
Collectivism describes ideology (political or otherwise) that favors the collective, like-wise Individualism describes ideology that favors the individual.

Some claim the Second Amendment, like the Three-Fifths Compromise, was ratified to preserve slavery. This is only partially true.

We explain populism, globalization, nativism, nationalism, neoliberalism, modernization, and other terms important for understanding modern world politics.

The Federalists and Anti-Federalists were the first political factions of the U.S.. They arose out of a debate over the ratification of the 1787 Constitution and went on to form the basis of our current two-party system.

Switzerland doesn’t require its citizens to own guns. Guns are regulated in three classes and there is mandatory military service for able-bodied men.

It is a myth that your vote doesn’t count. Despite the electoral college electing the President directly, every vote counts. It just counts in complex ways that differ by election, state, and region.

America’s founding fathers were classical liberals, this means they favored liberty, private property, capitalism, freedom of religion, and a limited Republican style of government.

Classical liberalism arose in opposition to state-imposed religion and aristocracy in the 1600 – 1700’s during the Age of Enlightenment in Europe and America.