The Difference Between Truth and Facts

Truth and facts have a lot in common, but they are not exactly the same. Truth is something that is the case. Facts are true statements. Truth is best described using facts and logical reasoning.
Reason and logic are two closely related forms of thinking involving the comparison of terms which can be studied in terms of mathematics or philosophy and can be considered together as well as apart.
Or more poetically:
Enlightenment, in then in this respect, is the “ends” of using logic and reason to shed light on that which we would not otherwise know. The change between not knowing and knowing. See the Cave metaphor.

Truth and facts have a lot in common, but they are not exactly the same. Truth is something that is the case. Facts are true statements. Truth is best described using facts and logical reasoning.

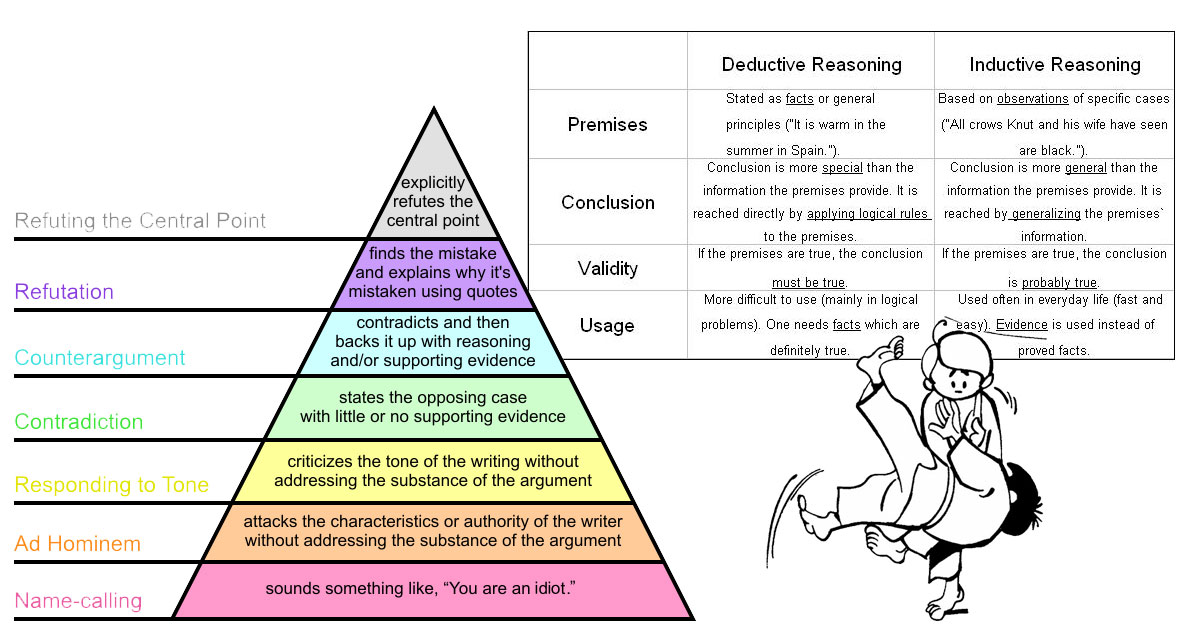
Deductive, inductive, and abductive reasoning are three basic reasoning types. In simple terms, deductive reasoning deals with certainty, inductive reasoning with probability, and abductive reasoning with guesswork.

Facts are things that are the case for sure, they are stated plainly and without bias. Opinions meanwhile inject subjectivity and bias. Since most content in any form contains at least some subjectivity and bias, it is rare to find pure facts and common to find opinion.

In simple terms, analysis examines a system by dividing a whole into its parts, and synthesis examines a system by combining and comparing parts.
We explain inductive reasoning, a bottom-up reasoning method that reasons by consistency, comparing particulars and probabilities to find likely truths.
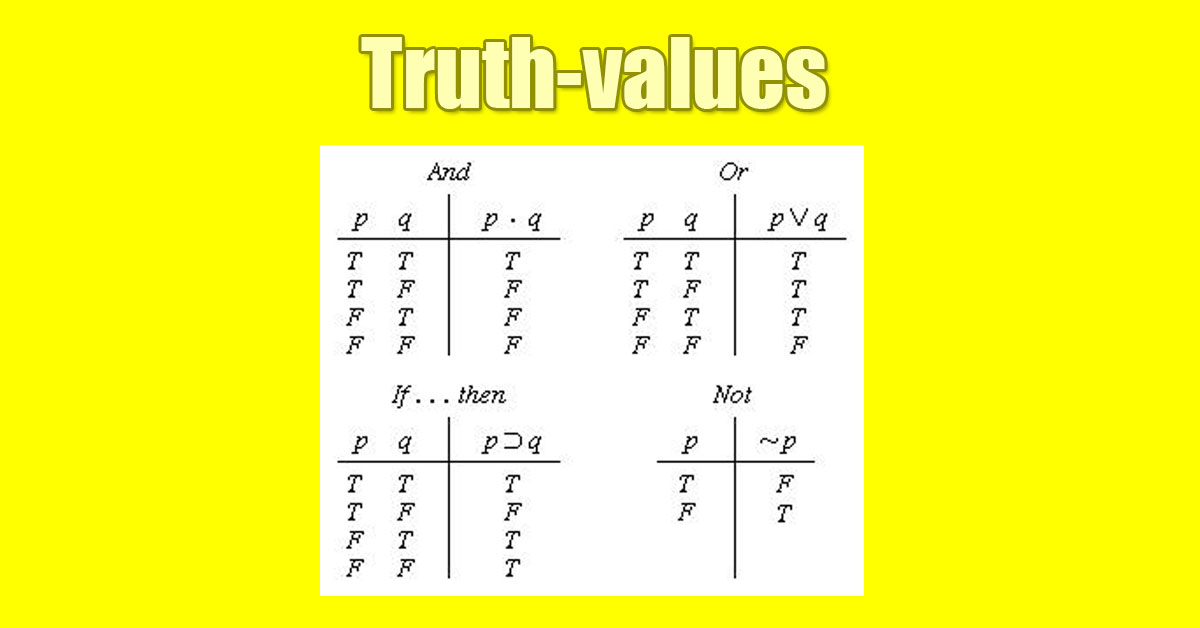
A truth-value is a label that is given to a statement (a proposition) that denotes the relation of the statement to truth.

We present a system of “logical, epistemological, and ontological categories of being and knowledge” (categories to place all empirical and rational concepts into).
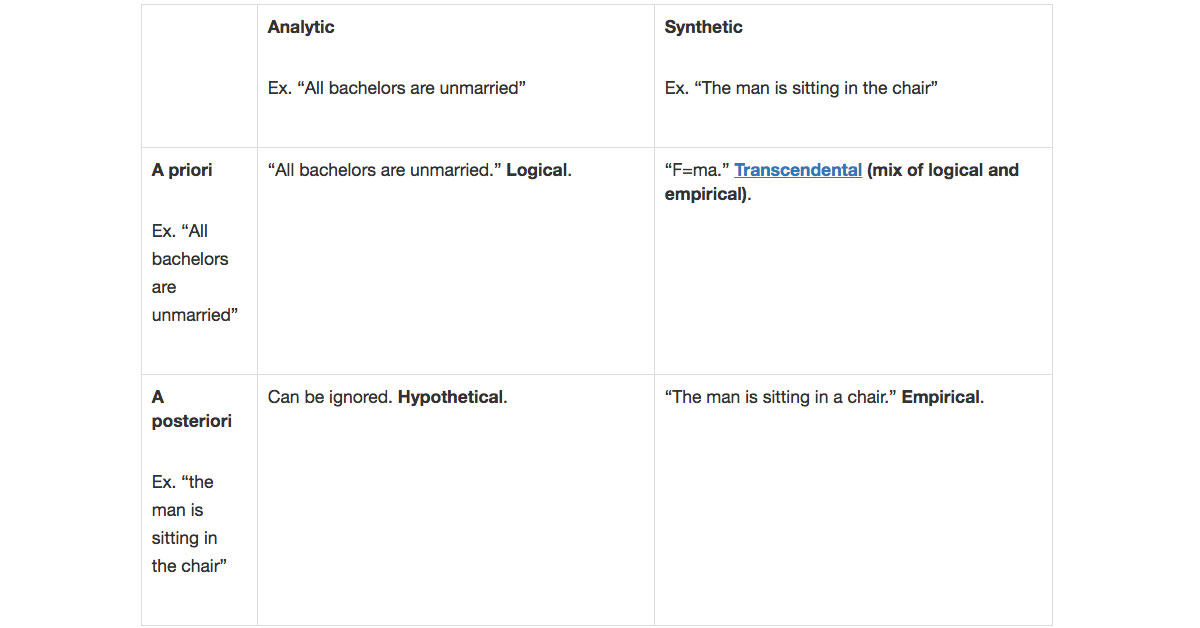
We explain the a priori-a posteriori distinction, analytic-synthetic distinction, necessary-contingent distinction and other logic-based terms.
We present a list of types of propaganda, propaganda techniques, and propaganda strategies used to manipulate public opinion in the modern day.
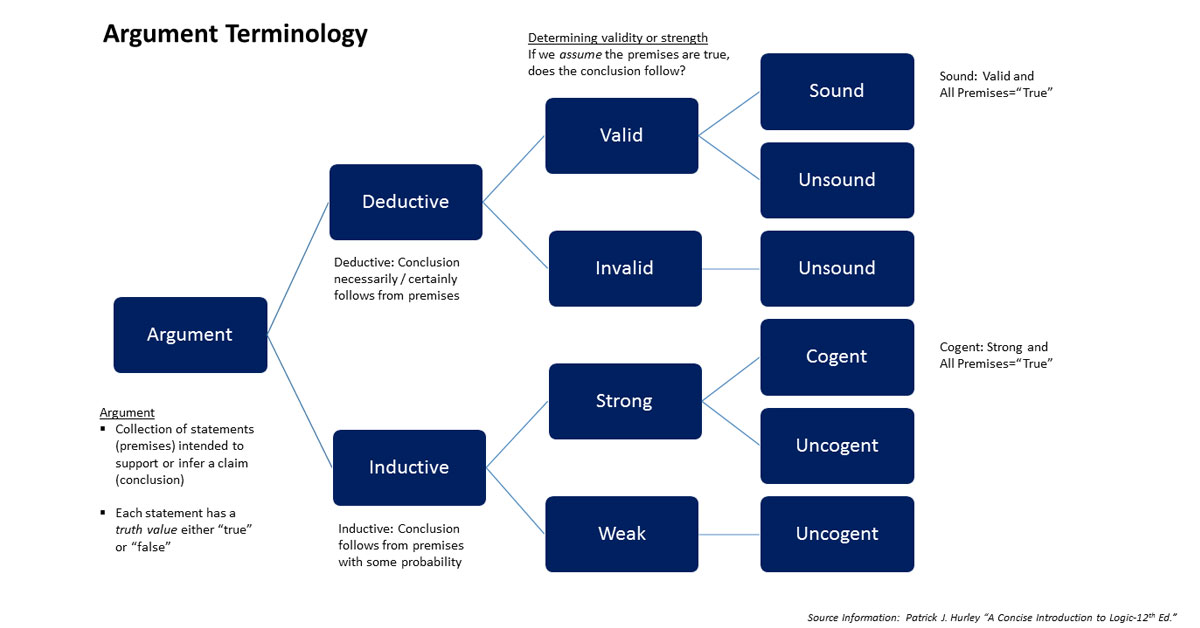
We explain and compare the different types of reasoning methods including deductive, inductive, abductive, analogical, and fallacious reasoning.