John Locke is the Father of Liberalism

John Locke can be considered the father of liberalism. His theories on life, liberty, property, consent, and the social contract form the foundation of classical liberalism.
Society and Social Sciences is a broad category referring to the relationships between networks and groups of people, and the study of this.

John Locke can be considered the father of liberalism. His theories on life, liberty, property, consent, and the social contract form the foundation of classical liberalism.

Usury (charging interest in moneylending, especially at high rates) used to be viewed as a sin by many religions and was banned by many cultures.

In Spanish, double letter usage indicates a plural. For example, the U.S. (United States) is EE. UU., or E.E.U.U., or simply EEUU (Estados Unidos) in Spanish.

“Civil Religion” is the civic “religion” of a nation. It doesn’t describe the theological religion of a nation, but rather a quasi-religious shared identity built around national symbolism and customs.
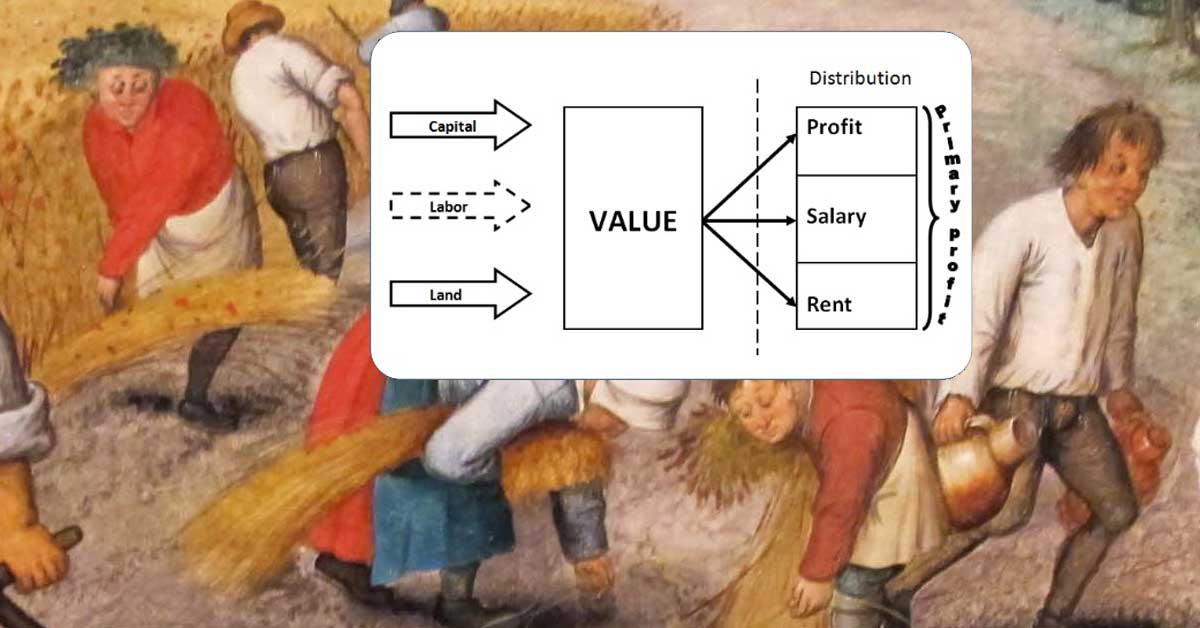
As John Locke and Adam Smith elude, physical work creates private property and gives possessions exchange-value (value in a trade).
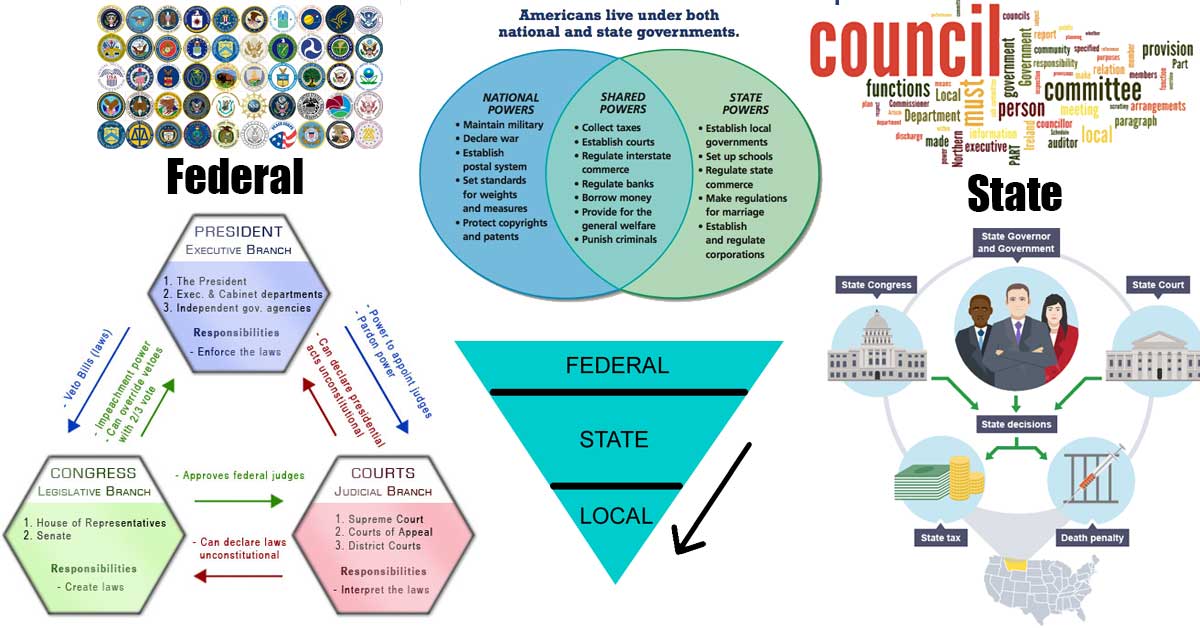
Separation of Powers describes the way in which government is divided into different branches (ex. in the U.S., the legislative, executive, and judicial). Checks and balances describe the powers each branch has to “check” the other branches and ensure a balance of power.
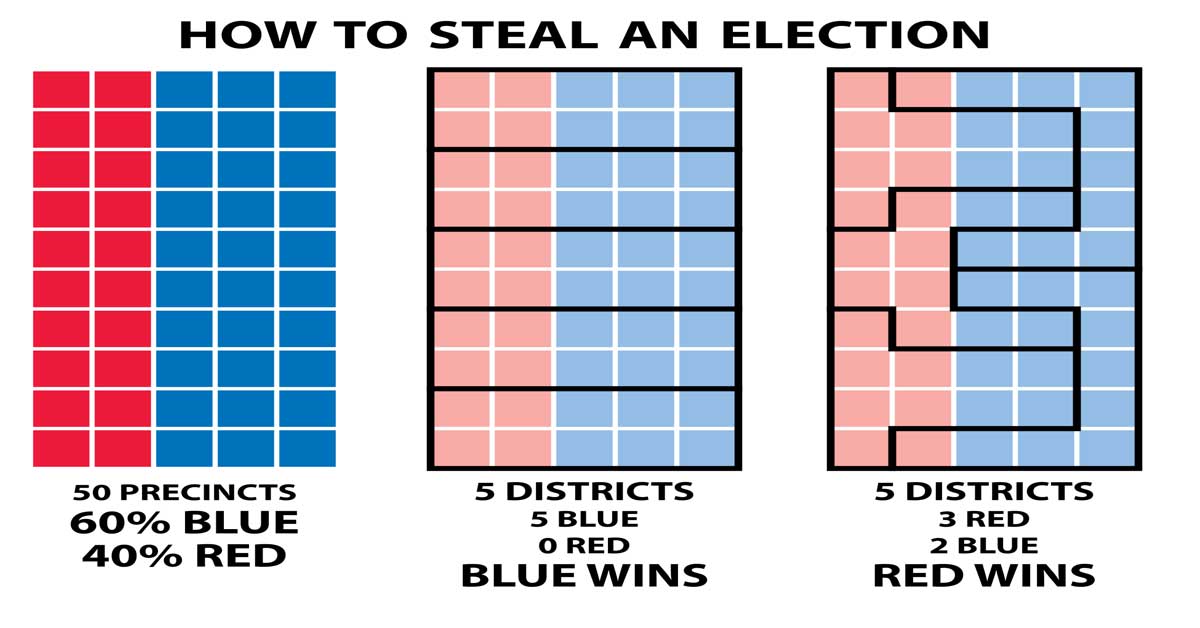
Voter fraud is real and so is voter suppression. However, widespread voter fraud is very unlikely to occur, and convicted voter fraud in the United States is very uncommon.
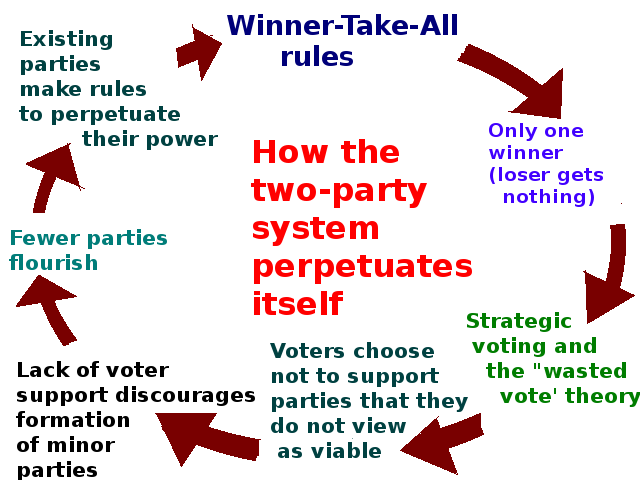
We explain political duopolies by looking at the political duopoly in the United States of America and other historic duopolies.
In modern history political factions have often been represented by a color, we look at political color to understand color politics.

In America we have a Progressive Federal Income Tax system broken down into “tax brackets”. Tax Filers pay the “marginal tax rate” on each dollar of income in a given bracket (after most deductions, but before tax credits).